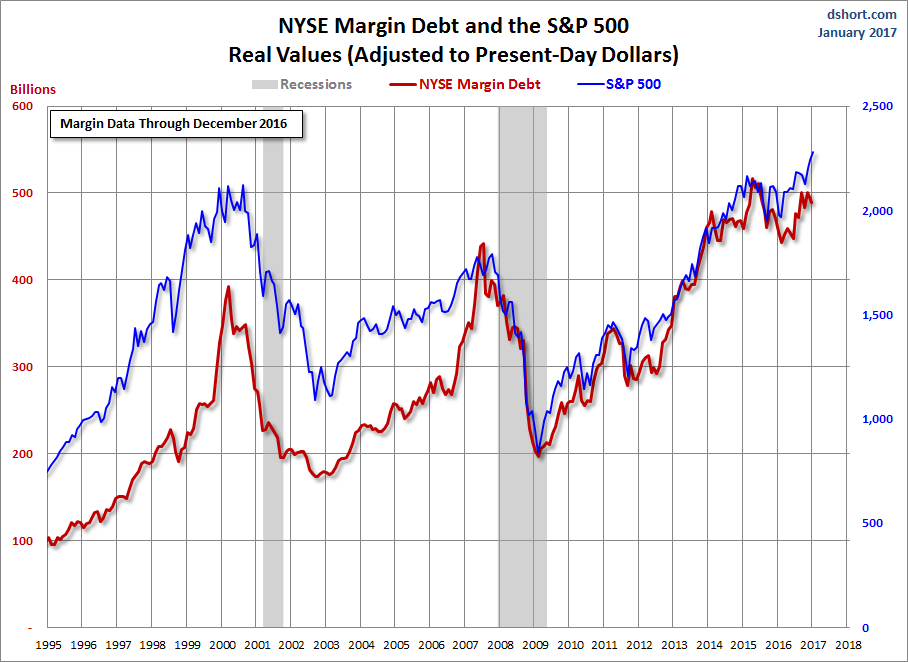
1. Margin debt has increased 193% since the bull market began—the same as the rise from 2002 to 2007.
1. Margin debt has increased 193% since the bull market began—the same as the rise from 2002 to 2007.
Michael Belkin called the 2000 market top. Now the publisher of the Belkin Report, an institutional newsletter on asset allocation, and the Belkin Gold Stock Report is waving a warning flag about the level of margin debt on the New York Stock Exchange.
Margin debt is the loans banks and brokerages make to investors, using their stock- and bond-holdings as collateral. In November, it neared an all-time high of $507 billion and has hovered close to that level since. “It’s something that’s hanging over the market,” he says. “The market is addicted to debt.”
There’s precedent for a high level of margin debt foreshadowing a market collapse. It peaked in March 2000, congruent with the market’s March 24 top and subsequent 49% decline. And it peaked again in July 2007, a few months before the market top in October. Another disturbing factor: The percentage rise in margin debt over the latest bull market is 193%, exactly the increase from 2002 to 2007, when the financial crisis began and the Standard & Poor’s 500 index later fell 57%.
The problem with margin debt is that it causes a cascade effect. As the market falls, investors get margin calls on their loans and have to sell stocks to maintain their margin-debt minimum.
Ed Yardeni, president of Yardeni Research, says, “As long as the market is going up, margin debt tends to go up as well.” And margin debt exacerbates a bear market. But Yardeni doesn’t know of any time when margin debt triggered a bear market. That’s a relief.
http://www.barrons.com/articles/is-margin-debt-a-bear-market-indicator-1487394796
The NYSE has released new data for margin debt, now available through December. The latest debt level is down 2.2% month-over-month. The current level is 3.5% below its record high set in April 2015. The December data gives us an additional sense of investor behavior during the election rally.
https://www.advisorperspectives.com/dshort/updates/2017/02/01/a-new-look-at-nyse-margin-debt-and-the-market
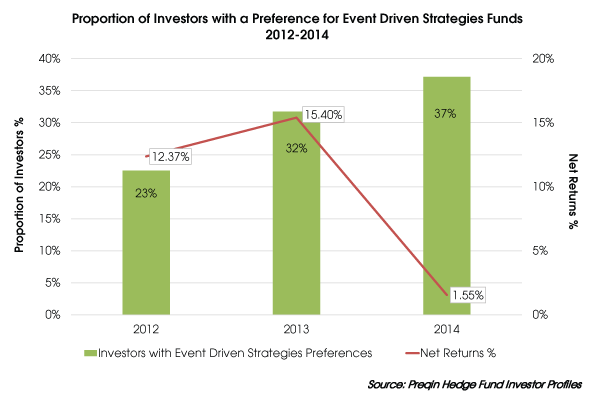
2.Event Driven Hedge Funds Lost $38B Last Year.
Event-driven hedge funds, a strategy which encompasses betting on mergers, lost $38.3 billion in net assets last year, according to data tracker HFR. Hedge funds focusing on merger arbitrage returned 3.6% last year, as per HFR.
As popularity increased, returns decreased.
 http://www.slideshare.net/elitedealmaker/event-driven-hedgefunds
http://www.slideshare.net/elitedealmaker/event-driven-hedgefunds
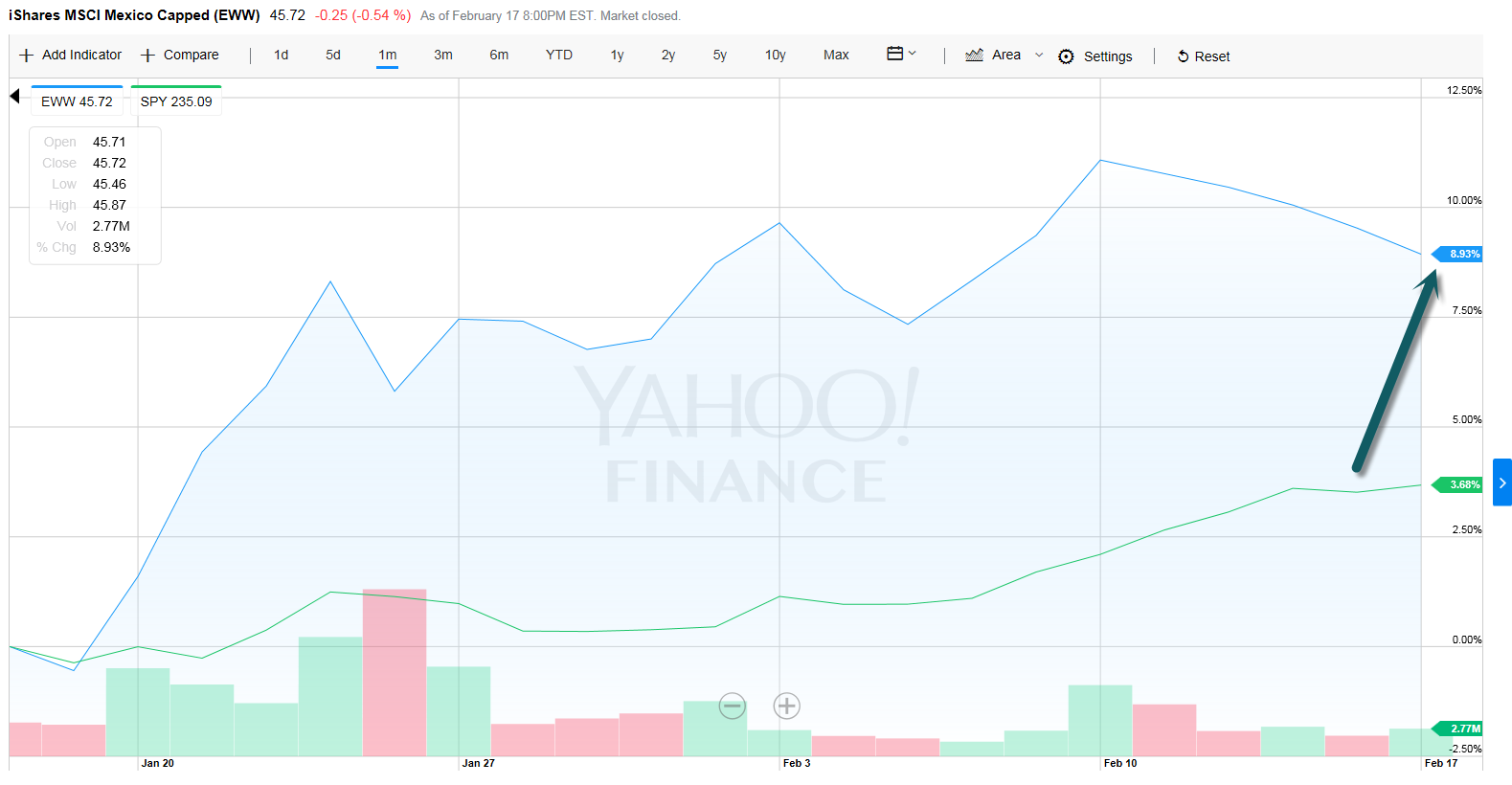
3.Since Inauguration…Mexico is Best Performing Country ETF….+8.93% vs. S&P +3.68%
www.yahoofinance.com
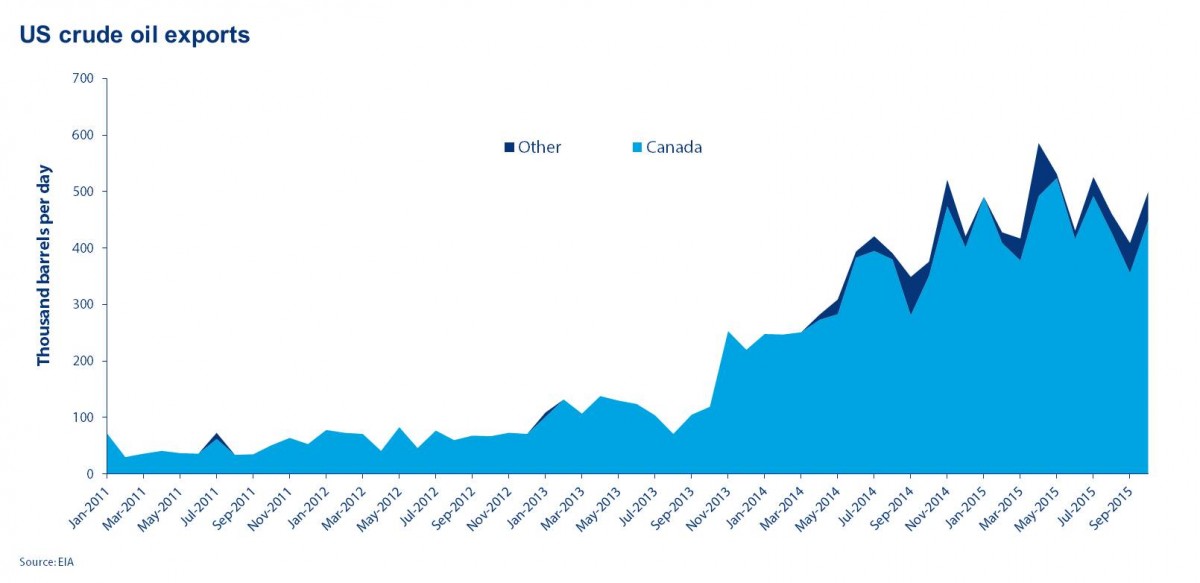
4.U.S. Crude Exports Competing with OPEC for Asian Market Share.
BMI Research notes crude exports from the U.S. reached a record high in the week ended February 10, with most of the volume directed to Asia — the fastest growing market and the longstanding battleground for OPEC nations.
In fact, OPEC’s top producers are prioritizing trades with Asia over the U.S. and Europe in order to maintain market shares, the firm added.
“You can say the U.S. is the counterforce against OPEC,” said Vivek Dhar, a commodities strategist at Commonwealth Bank of Australia.
— Georgi Kantchev contributed to this article.
http://www.marketwatch.com/story/oil-prices-rise-as-investors-increase-bullish-bets-on-prices-2017-02-21
 5.Venture Capital 20% Off Highs.
5.Venture Capital 20% Off Highs.
Zerohedge
Few business communities swing from boom to bust as reliably as Silicon Valley, but detecting shifts in this opaque world can be challenging. To help illuminate the field, Bloomberg created the U.S. Startups Barometer, a new weekly indicator that tracks the overall health of the business environment for private technology companies based in the U.S.
So how ‘healthy’ is the American Venture Capital business?
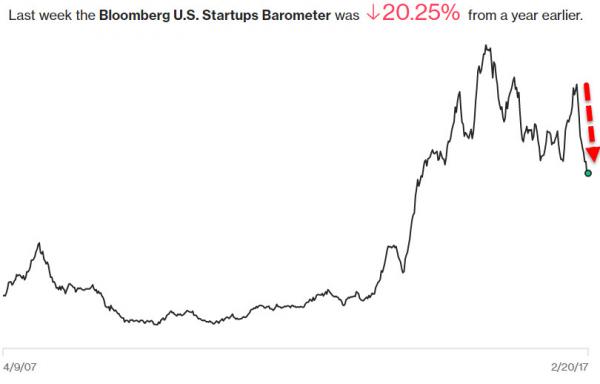
http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2017-02-20/death-venture-capital
6.95% of Foreign Investors Plan to Maintain or Increase Investment in U.S. Real Estate.
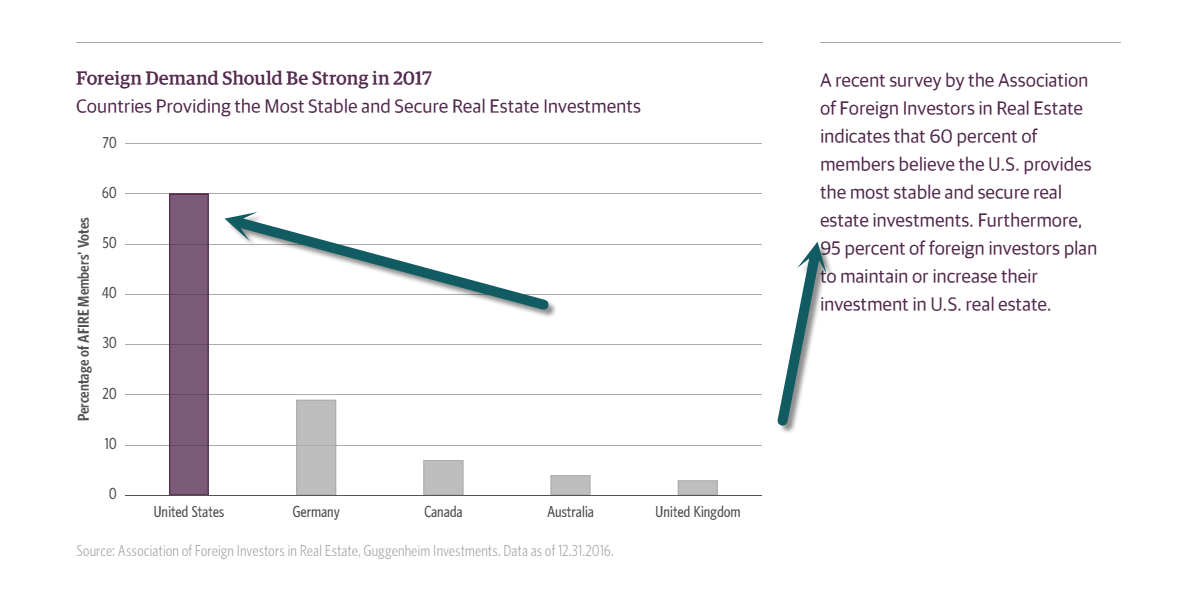
https://www.guggenheimpartners.com/perspectives/portfolio-strategy/fixed-income-outlook-first-quarter-2017?utm_source=pardot&utm_campaign=fixed%20income%20outlook%20q1%202017&utm_medium=email&utm_content=portfolio%20strategy
7.The U.S. is a Young Country….Think about this Regarding New York or Shore Real Estate
It now takes an average of nearly 26 years for a couple living in London with one child to save for a home deposit.
House prices have been rising steadily across the UK for several decades, but they have increased most dramatically in the capital, where the average first-time home now costs £402,692, according to research by Halifax Bank.
On top of that, Halifax found that the cost of a first-time buyer deposit has nearly quadrupled in the last decade, from £26,701 in 2006 to £100,445 last year.
That means, for an average couple with one child, it will take more than a quarter of a century of saving to buy a home. Even without a kid in tow, you’re looking at nearly 14 years.
Take a look at the chart from Barclays latest Housing Chartbook below, which uses data from the Redfern Review:
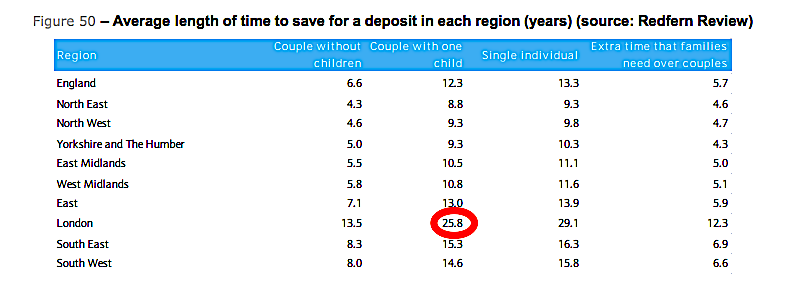
Barclays Housing Chartbook
The evidence is striking: big house prices, huge deposits, and unprecedented falls in real wage levels across the UK since the 2008 financial crash mean that it is now unrealistic for many first-time buyers to get on the property ladder until they are well into their forties.
http://www.businessinsider.com/average-london-couple-with-child-spends-26-years-saving-for-a-deposit-2017-2
8.Boom and Bust…We are Facing Labor Shortages in Construction.
United States: US homebuilders are struggling to find skilled workers, which is delaying numerous projects. Since the housing crisis (that started in 2006) younger workers have been discouraged from entering the field (and getting the appropriate training). Now the industry faces labor shortages.
Source: NAHB, @dietz_econ; Read full article
9.Read of the Day….Follow Up to My Solar Comments Last Week.
GE, IBM, And Other Top Corporates Are Working On
86
Deepashri Varadharajan
FollowDeepashri Varadharajan
Analyst & Writer at CB Insights
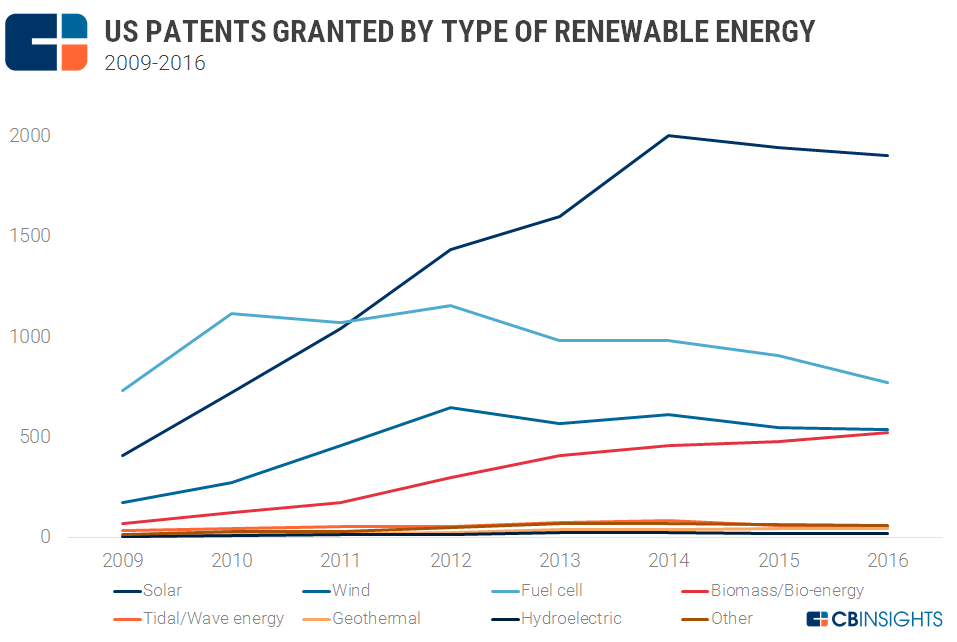
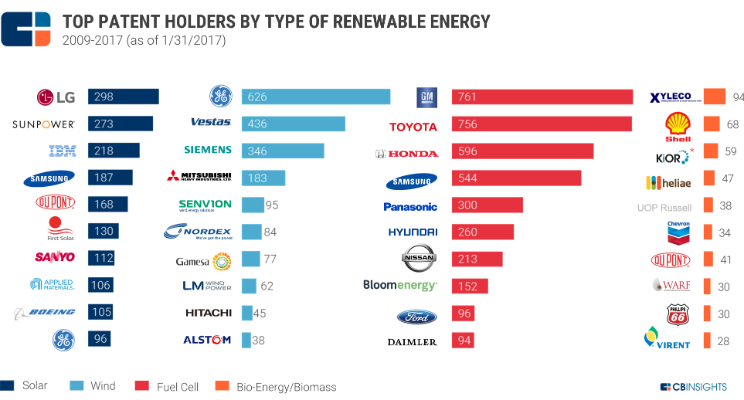
The majority of the patents granted since 2009 have been in solar energy. Toyota emerged as the top patent holder with its fuel cell research.
Renewable energy had a big year in 2016. Prices of solar power dropped, making it cheaper than coal in parts of the world and key corporates backed alternative energy in various ways. Tesla acquired SolarCity for $2B; and in Q3’16 General Motors pledged to “generate or source all electrical power for its 350 operations in 59 countries with 100% renewable energy — such as wind, sun and landfill gas — by 2050.” Google announced it would switch to 100% renewable energy in 2017.
To study the growing interest in this space and the technological advancements in clean energy, we analyzed over 50,000 US renewable energy patent grants and applications between 2009 and 1/31/2017.
This report contains the following sections:
Annual renewable energy patents granted
Patents granted by type of renewable energy
Top patent holders
Top patent holders by type of renewable energy
Trends in renewable energy patent application activity
The results are based on keyword searches of the CB Insights database for various renewable energy technologies, including solar, wind energy, geothermal energy, hydroelectricity, fuel cells, bio-energy and tidal/wave energy. Toyota emerged as the top patent holder, with 800 patents under its belt, mainly in fuel cell technology. Although most of the top patent holders are big corporations, Taiwan-based Industrial Technology Research Institute made it to the list of top 22 patent holders. Overall, solar patents accounted for 42% of all renewable energy patents granted during the time period.
Note: Dates in first section of analysis are based on the date when the US patent office approves an application for patent, i.e. a grant. Dates in latter section of analysis are based on the date when patent applications were submitted by individuals or companies.
Annual renewable energy patents granted
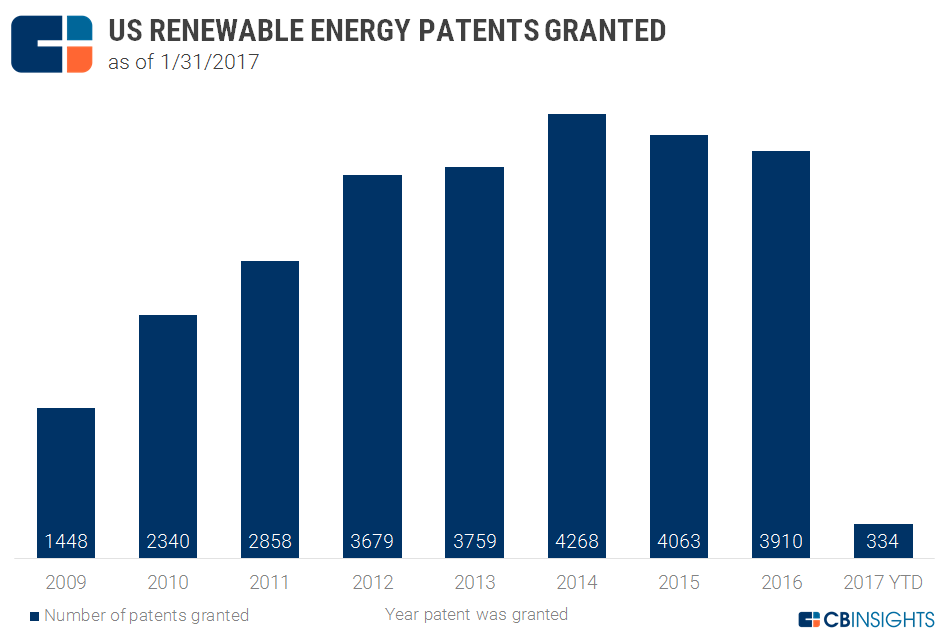
More than 26,000 patents related to renewable energy have been approved by the United States Patent Office or USPTO since 2009.
The year 2014 saw the highest number of renewable energy patents granted, at 4,268. The numbers dropped slightly in 2015 and 2016 to 4,063 and 3,910, respectively. So far in 2017, 334 patents have been approved, including Google’s technology for an antenna with a solar panel, an LG Innotek solar cell apparatus, a General Electric system for reducing vibration in a wind turbine, a wind turbine blade design by Siemens Energy, and a Toyota technique for increasing the production of plant biomass.
Patents by type of energy: Solar leads the way
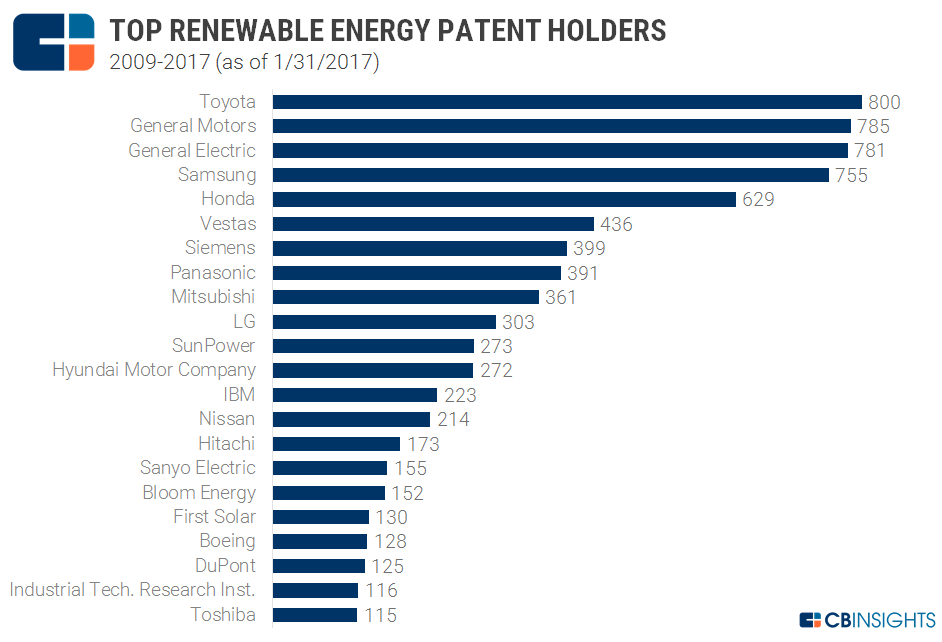
Solar patents have dominated the total share of renewable energy patents since 2012. Solar technology accounted for 42% of total patents granted. Fuel cell and wind energy accounted for 29% and 15% of patent share, respectively.
This is in line with investor interest in private solar companies. Equity deals to solar startups are higher than deals to wind and other types of renewable energy companies.
The number of solar patents granted dropped in 2015 to 1,942 from 2,002 the previous year. The numbers dropped further to 1,906 in 2016. Bio-energy patents, meanwhile, reached an 8-year high in 2016 at 524. January 2017 saw an additional 37 bio-energy grants, including patents granted to corporations like Mitsubishi, Toyota, and Sony.
Geothermal energy patents have gradually increased, from less than 10 in 2009 to over 40 in 2015 and 2016. To name a few, a Microsoft patent explores geothermal cooling for its data center, while Fuji Electric and Chevron USA received 2 patents each last year that utilize geothermal energy.
The “Other” category includes hybrid energy systems that utilize more than one energy source.
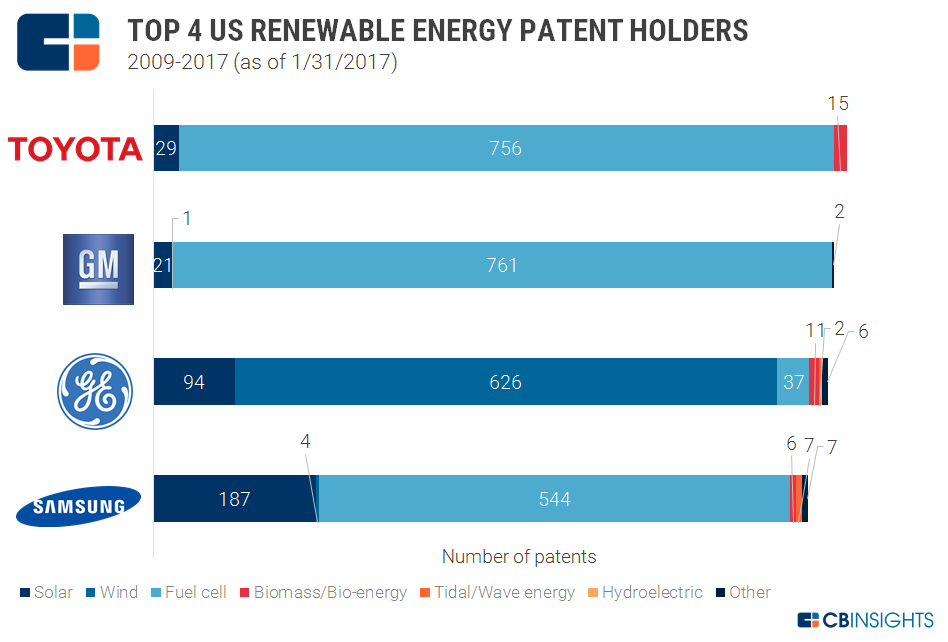
Top patent holders: Toyota, GM push for fuel cells
Toyota was the top patent holder in renewable energy technologies, with 800 patent grants to its name since 2009. General Motors ranked second, followed closely by General Electric and Samsung.
Almost all of Toyota’s patents, around 95%, have been in fuel cell technologies. Fuel cells convert chemical energy to electricity, and can be considered renewable energy assuming the fuel (hydrogen) is derived from a renewable source. In 2015, the auto giant opened more than 5,000 of its global fuel cell patents for royalty-free licensing by other auto makers and fuel cell-focused companies. The rationale was to help speed the development of a fuel cell ecosystem:
The first generation hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, launched between 2015 and 2020, will be critical, requiring a concerted effort and unconventional collaboration between automakers, government regulators, academia and energy providers. By eliminating traditional corporate boundaries, we can speed the development of new technologies and move into the future of mobility more quickly, effectively and economically.” – Bob Carter, SVP of automotive operations at Toyota Motor Sales
General Motors followed a similar trend, with 761 fuel cell patents.
General Electric, on the other hand, has placed its bets on wind energy, with over 626 patents in this category out of 781 patents granted so far.
Here’s a breakdown of the patents of the top 4 renewable energy patent holders on our list based on the type of renewable energy:
10.In Defense of Duty
Duty and responsibility have lost stature to autonomy and creativity–Alas.
Posted Feb 19, 2017
Source: Pixabay, CC0 Public Domain
When I say the word “duty,” how do you feel? For many, “duty” evokes a negative response—The word seems militaristic, even fascist, certainly a restriction of a person’s autonomy.
Duty’s negative image is unfortunate because, over the millennia, duty has yielded great benefit, whether a duty to family, community, or the world. Without being driven by duty, more spouses would run from family responsibility. More residents would leave for safer surrounds, leaving their community to sink further. More people would prioritize selfish pleasures over trying to make the world a better place. And yes, that includes military duty. The world might today be run by Nazis if not for the countless soldiers willing to sacrifice pleasure and risk their lives because of duty.
I define duty as the willingness to replace the pursuit of happiness with the pursuit of contribution, a willingness to forgo personal pleasure in the service of a larger good, to be comfortable with being uncomfortable if it will likely yield greater benefit to one’s sphere of influence.
Alas, I believe that duty’s importance has diminished in recent decades, perhaps spawned in part by the pleasure-first ‘60s and its hub of drugs, dropping out, and rebelling against authority. Today, autonomy and artistic creativity, even eccentricity, seem more valued than duty and its offshoots: responsibility, discipline, and respect for authority. I believe duty deserves a more exalted place in our hierarchy of values.
Might you want to look inward to decide if you are too focused on the pursuit of happiness over the pursuit of contribution, of duty? Are you too concerned with escaping from discomfort than with accepting a measure of discomfort in exchange for making a bigger difference?
Duty isn’t all about self-sacrifice. It enables you to put your head on the pillow each night feeling good about the life you’re living and, at your life’s end, feeling good about the life you’ve led.
I’ve created a short video that addresses this issue.
If you might like career or personal coaching from Marty Nemko, email him a brief description of your situation: mnemko@comcast.net(link sends e-mail).
https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/how-do-life/201702/in-defense-duty