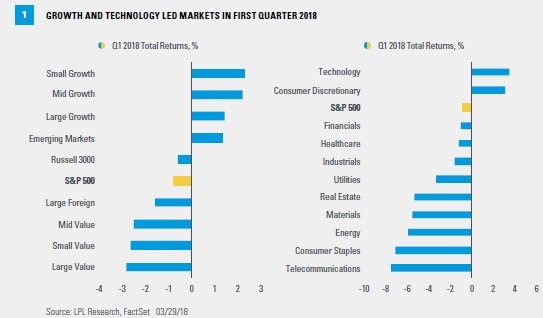
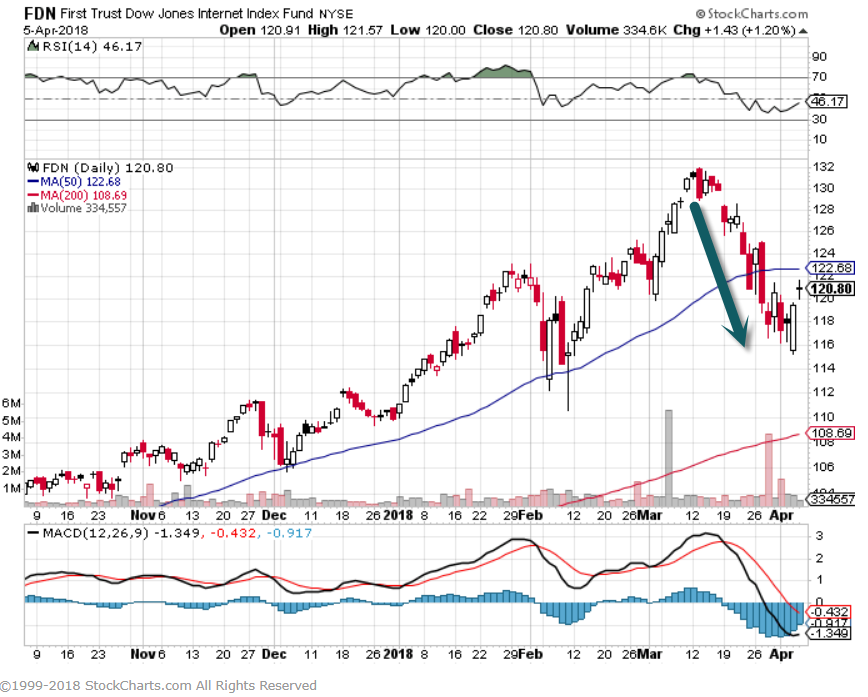
1.Chinese Venture Funding is 15x 2013 Levels….2017 Saw Almost Equal Funding to U.S.
Silicon Valley Powered American Tech Dominance—Now It Has a Challenger
An exclusive WSJ analysis shows how venture-capital investment from Asia is skyrocketing, threatening to shift power over innovation
By Phred Dvorak and Yasufumi Saito
Silicon Valley, long the undisputed king of venture capital, is now sharing its throne with Asia.
A decade ago, nearly three-quarters of the world’s financing of innovative, tech-heavy startups and young companies took place in the U.S., with American investors plowing money into mostly U.S.-based venture firms.
Now, a surge of new money—mostly from China—has helped drive funding totals into the stratosphere and has transformed the venture landscape, according to an exclusive Wall Street Journal analysis of venture funding data.
Asian investors directed nearly as much money into startups last year as American investors did—40% of the record $154 billion in global venture financing versus 44%, the Journal’s analysis of data from private markets data tracker Dow Jones VentureSource found. Asia’s share is up from less than 5% just 10 years ago.