1. VIX No Spike Yet…2008 and Covid Had Big VIX Spikes.
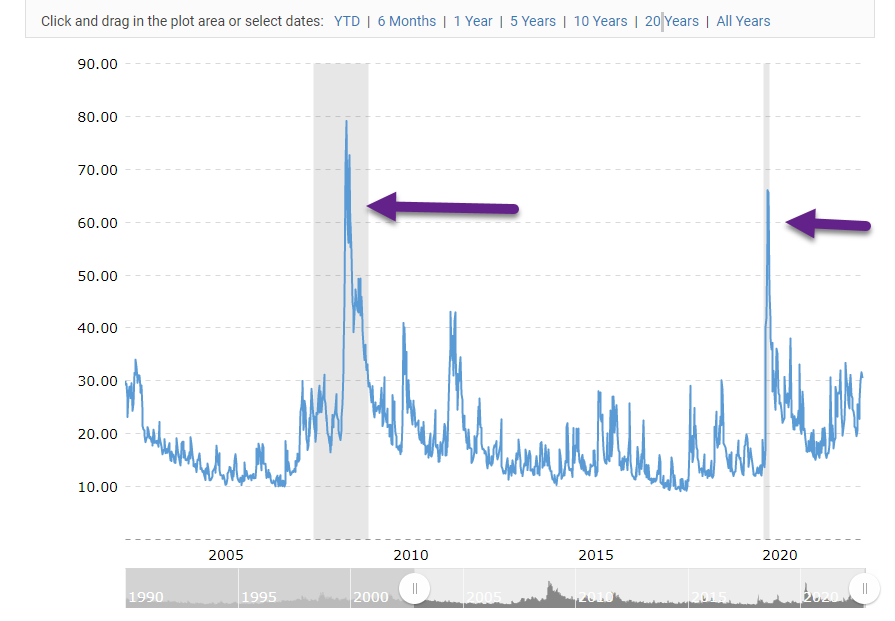
https://www.macrotrends.net/2603/vix-volatility-index-historical-chart
2. Crash Confidence Indicator from Robert Shiller …First Time I Saw this Indicator.
To appreciate the strength of this contrarian indicator, consider the data in the table below. It contrasts the average S&P 500 SPX, -0.04% total real-return in the wake of either the 10% of months when crash anxiety was highest or the decile when that anxiety was lowest. The differences are significant at the 95% confidence level that statisticians often use when assessing whether a pattern is genuine.
| Crash confidence index readings: | Fear of crash is… | Average S&P 500 total real return over subsequent 12 months | Average S&P 500 total real return over subsequent 2 years (annualized) | Average S&P 500 total real return over subsequent 5 years (annualized) |
| Lowest 10% of historical readings | Highest | 25.6% | 19.5% | 15.3% |
| Highest 10% of historical readings | Lowest | 5.6% | 6.6% | 6.1% |
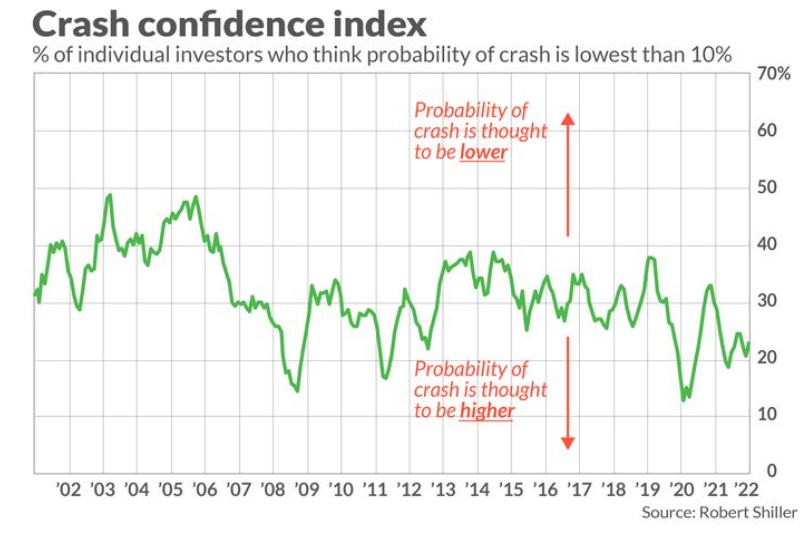
https://www.marketwatch.com/story/robert-shiller-created-an-index-that-shows-investors-fear-of-a-stock-market-crash-heres-what-its-saying-now-11665470643?mod=home-page
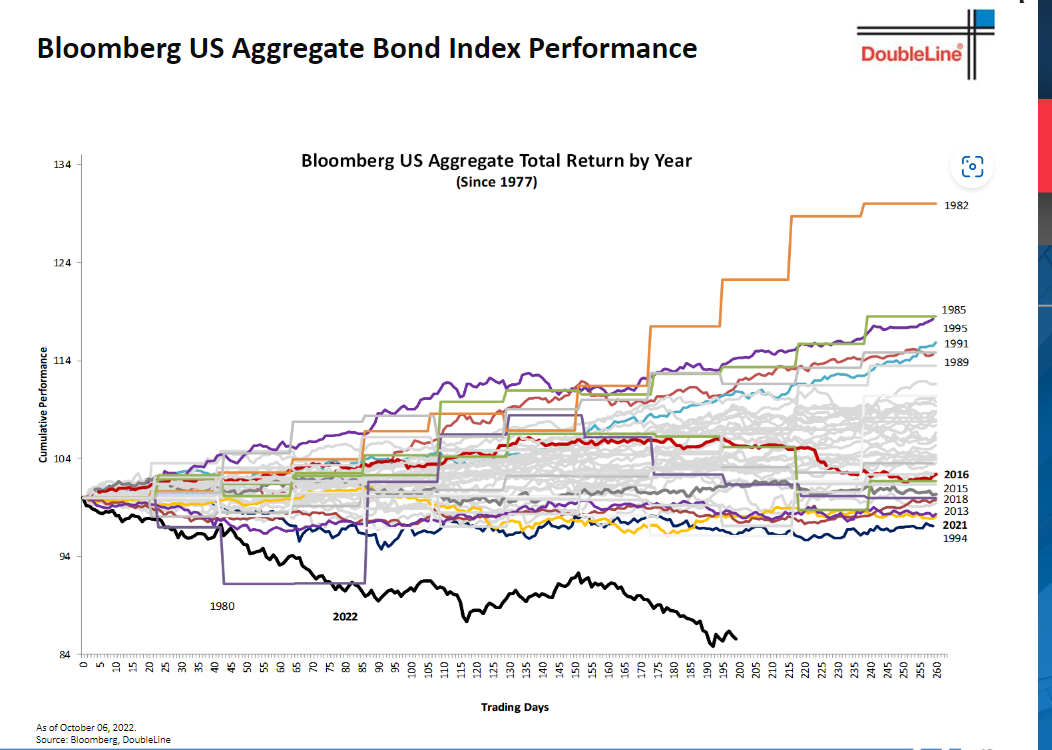
3. Bloomberg AGG Bond Index Worst Year Ever….-10% Worst Than Second Worst Year Ever.
Double Line Research
4. Intel and Cisco Charts Back to 1999 Tech Bubble Levels…..20 years of FLAT Performance.
These leaders of Internet bubble never regained highs again, maybe a lesson to Millennials on chasing the last bull markets winners (FAANG).
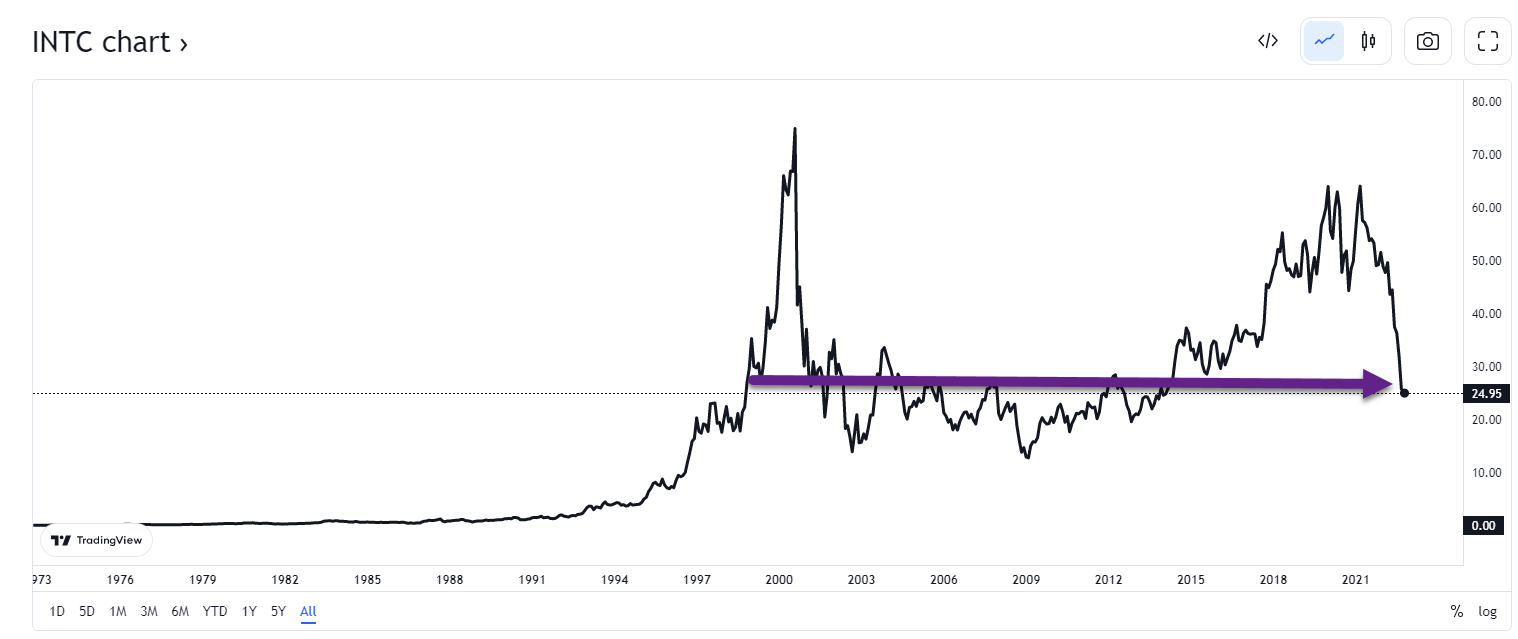
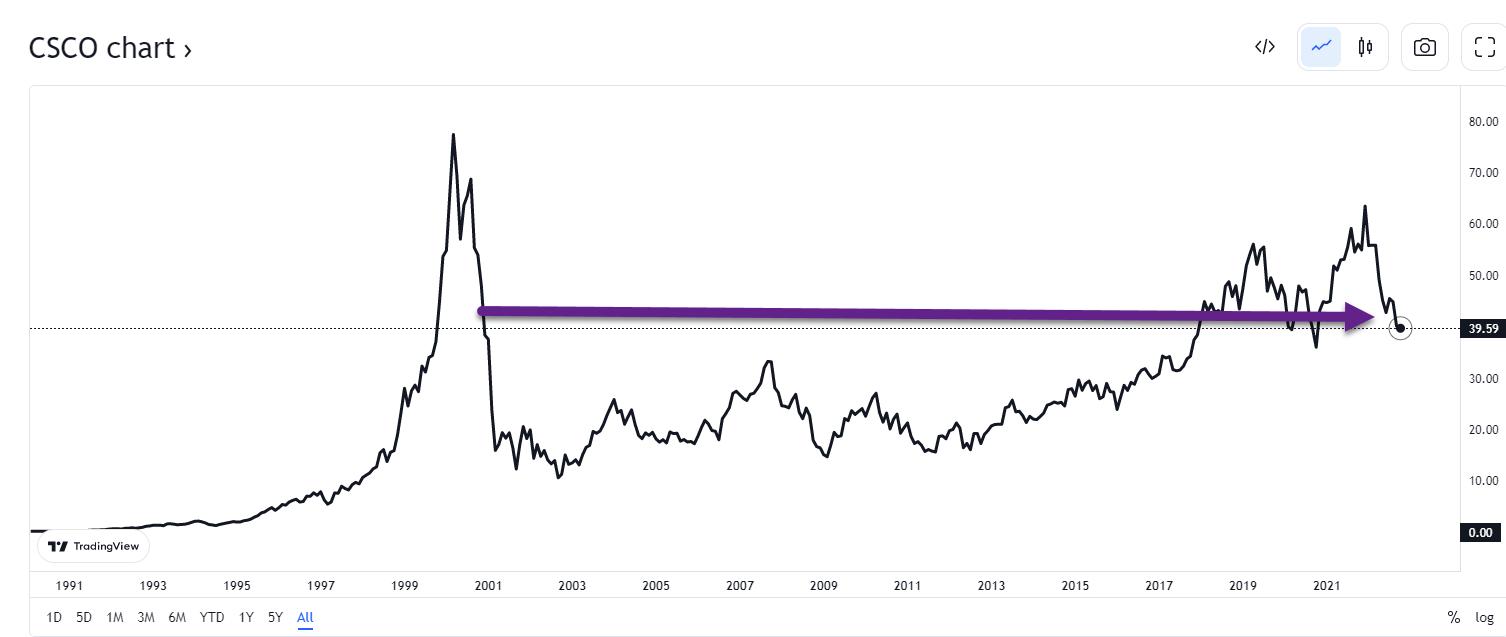
Trading View Charts https://www.tradingview.com/
5. International Bond Index Breaks to New Lows.
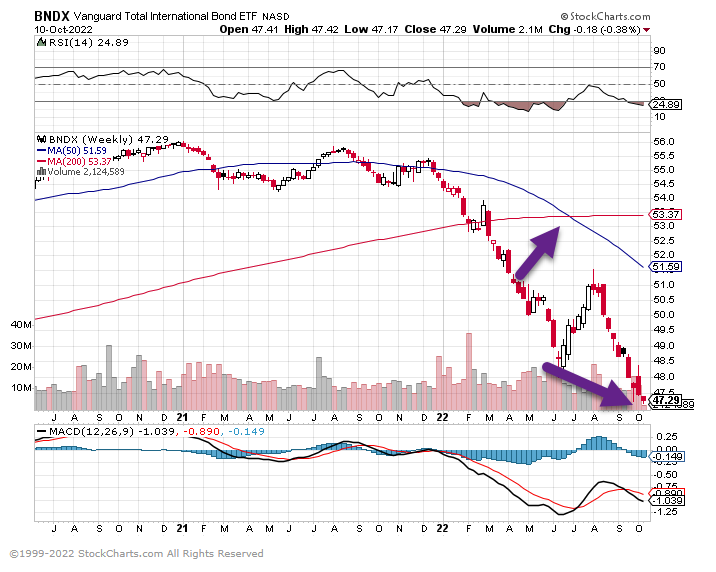
6. QQQ New Lows and Hard Close Below 200 Week Moving Average
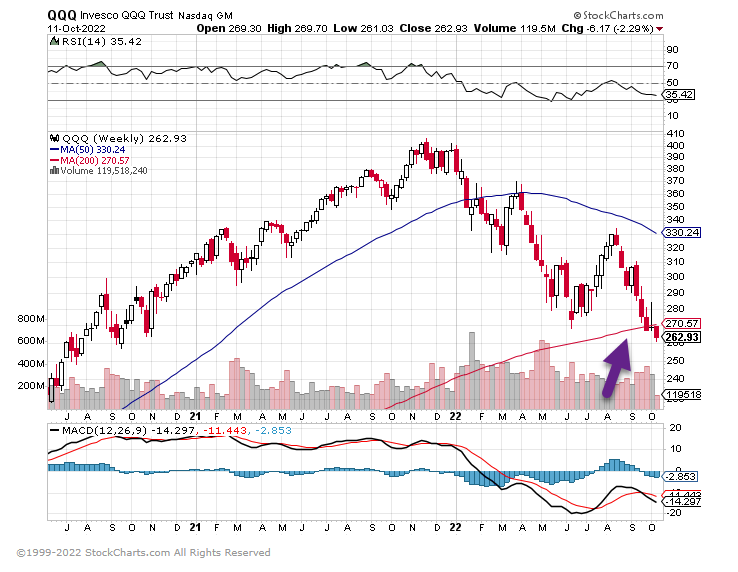
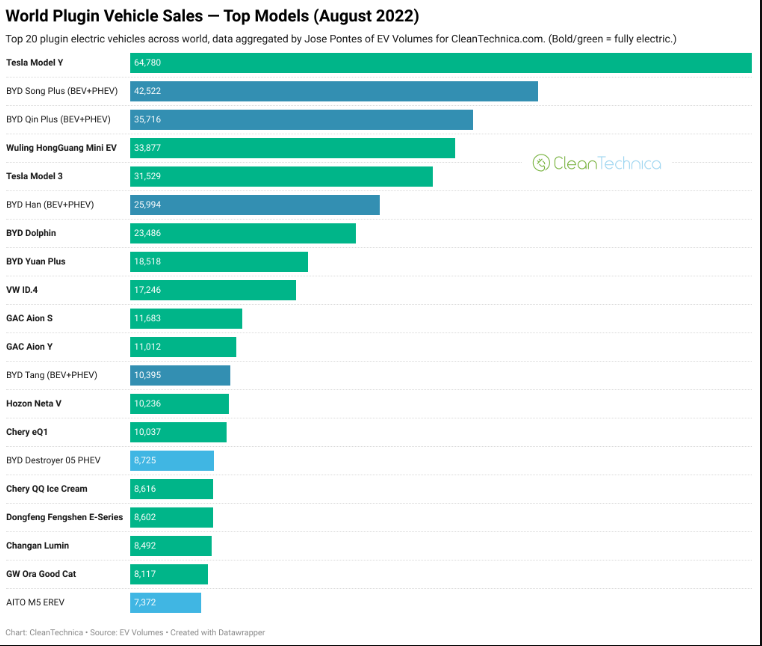
7. Software ETF New Lows.
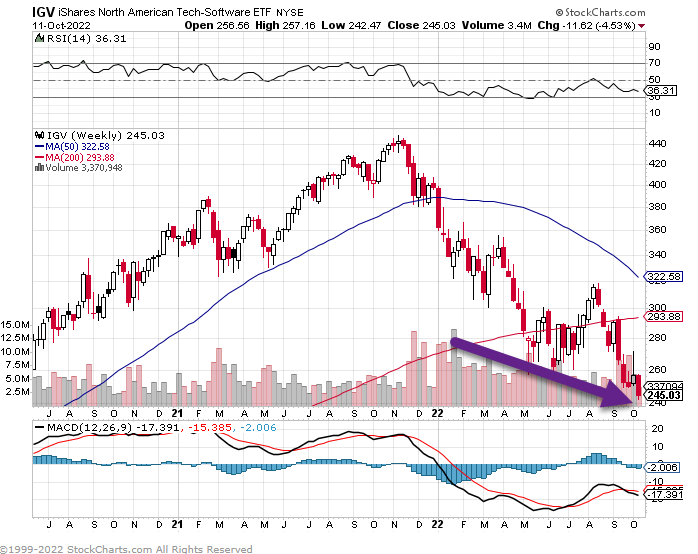
8. 100% Electric Vehicles = 11% Of New Vehicle Sales Globally!
And 15% of new vehicles sold across the world have a plug. By
Global plugin vehicle registrations were up 60% in August 2022 compared to August 2021, reaching 847,000 units. This is the best result ever for an off-peak month (as in, not the final month of a quarter). So, expect not only that Q3 will be the best quarter ever for plugins, but also that September will provide the mother of all record months! I expect September will be the first time the world reaches one million plugin vehicle registrations in a month. With China (surely), the USA (likely), and Europe (maybe?) posting record months in September, expect the end of Q3 to be another time of celebration.
Year to date, the plugin share grew to 13% (9.2% BEV). That’s all great, but the internet loves lists, so here you go: The top 20 electric car sales leaders!
https://cleantechnica.com/
9. Five Ideas That Will Reshape Capitalism’s Next Century
From Advisor Perspectives By Adrian Wooldridge,
The Harvard Business Review is celebrating its 100th birthday with a fat book of its most influential and innovative articles and an electronic fanfare of videos, charts and online articles.
HBR was founded 14 years after its mothership, the Harvard Business School, to provide the fledgling discipline of business with a bit of academic heft. The new discipline faced a lot of sneering from the Brahmin establishment who ran Harvard in those days for lacking academic rigor as well as social cachet. Wallace Brett Donham, HBS’s dean from 1919 to 1942, hoped that the review would address one of these complaints by pioneering a “theory of business” based on rigorous research and capable of teaching fledgling businessmen sound judgment. Without such a theory, he wrote in the inaugural issue, business would be “unsystematic, haphazard, and for many men a pathetic gamble.”
Donham’s brainchild succeeded beyond anybody’s wildest dreams. HBR articles launched billion-dollar management ideas, such as re-engineering or asset-lite management, that changed entire industries. The few Brahmins who remain in Harvard look out from their little cubby holes at the business school across the river and gnash their teeth with envy. A magazine that was once described by one of its editors as being written by people who can’t write for people who can’t read is now a bible of corporate America.
Which is why the current volume is such a disappointment. The brief introduction makes a few interesting points— notably that the magazine’s focus has shifted from the tangible aspects of management, such as how to allocate financial resources or organize production, to more intangible subjects such as how to get the most out of your workers or enthrall your customers. But it fails to tackle any of the hard questions. Why is a discipline that is supposed to make business less of a haphazard gamble subject to so many fads and indeed frauds? And how does HBR explain its role in promoting ideas such as re-engineering or companies such as Enron? The HBR doesn’t necessarily owe us humility, but it does owe us introspection.
The collection includes some great articles which it’s nice to have in one place (two of my favorites are the articles that bookend the collection, Peter Drucker on managing oneself and Gary Hamel and C.K. Prahalad on strategic intent). But it also contains some inexplicable gaps. How can you produce a collection of the most interesting and innovative articles in the HBR without including Michael Jensen’s “the eclipse of the public corporation,” an intellectual tour de force which defined an era? In general, the collection is ludicrously heavy on current preoccupations (such as authenticity) and light on yesterday’s passions (globalization as well as private equity). The book eschews chronological organization without embracing any thematic alternative that I could work out.
The extras are even more variable in quality. HBR asked some leading thinkers to speculate about what’s next for some big topics. Some of what they had to say was interesting (Ram Charam on the future of organizations); some was merely platitudinous (Marcus Buckingham on what a “good job” would look like). Where the package hit its nadir is about the future of management. HBR asked “a panel of global experts” what management will look like in the next 100 years. The answer that came back from each of the experts was almost identical: Management will become cuddlier and less command-and-control. Sut I Wong of the Norwegian Business School says that management will be all about “empathy.” Frederic Frery of ESCP Business School says that management will/should “forget about the art of war and focus instead on the art of seduction.” Rachel Spivey, the head of Google’s Stay & Thrive team, says that the future will be “all about fostering a direct, transparent and empathetic approach to management.”
What twaddle! I suspect the empathy-first approach that dominates today’s business schools will not survive the next five years intact let alone the next 50 or 100, or else will simply become so ossified that nobody outside a tiny clique will listen to it. Today’s focus on inclusion and empathy was dictated by the peculiar combination of a prolonged bull market on the one hand and the shock of the societal rifts exploited and widened by the Trump presidency. The focus will shift significantly in the future as recent preoccupations, notably diversity, become bureaucratized, and companies desperately adjust to the fracturing of the global economy, the rise of Asia and the long-term decline in productivity.
It would be churlish for me to be so brutal about the HBR panel’s predictions without offering some alternative predictions of my own (and with them my head, at least metaphorically, for anybody who wants to chop it off). I think that business life over the coming decades will be dominated by five great trends that will reshape management just as dramatically as did world wars, whether hot or cold, or the invention of the computer.
The return of a wartime economy
Vladimir Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has inaugurated a new era in business affairs, not just because it has forced business to respond to Russia’s immediate aggression but also because it has forced it to wake up to China’s geostrategic ambitions. President Xi Jinping will be further emboldened if, as is widely expected, he is effectively made president for life in the National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party. Competition between China and the West for resources, ranging from food, fish and water to rare earths, will only intensify as the world shifts to battery power and the war in Ukraine continues to threaten grain supplies.
So far most of the great initiatives have come from governments, particularly from the US government. President Joe Biden has passed a CHIPS Act to reduce dependence on Chinese semiconductors. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen has sung the praises of “friend-shoring.” Businesses are still playing catch-up — belatedly creating new supply chains in India or Vietnam to supplement their existing ones in China for example.
They will surely become more proactive as they adjust to a new world in which military spending is an increasingly powerful driver of the global economy and potential conflict an ever-present danger. A growing number of start-ups will shift their focus from consumer goods to military supplies. High-tech companies will follow the example of Palantir Technologies Inc. and challenge the power of companies such as Lockheed Martin Corp. and General Dynamics Corp. that were born before the digital age. Indeed, in the longer term a military-digital complex will likely replace the old military-industrial complex. Companies of all description, whether or not they are formally part of the digital-industrial complex, will beef up their political risk departments to pay more attention to military and strategic risks. Frederic Frery mocks the bad old days when “business strategy was often taught by military officers who looked to generals such as Sun Tzu and Carl von Clausewitz for management insights.” In fact, companies will turn to military men and women, schooled in hard realities at West Point and on the front line, for leadership and advice.
The great knowledge-worker cull
First, they came for the agricultural workers. Then they came for the industrial workers. Now they are coming for the knowledge workers. The great labor relations theme of the rest of the current century is that intelligent machines will do for workers by brain what dumber machines did previously for workers by hand — destroying their jobs, suppressing their wages, battering their psyches and generally driving them to the margins of society.
Techno-optimists like to put a positive spin on the march of the machines. Knowledge workers will become more productive by working with machines rather than against them, they said; machines would stop at the most sophisticated jobs — making leaps of imagination of thinking profound thoughts — thereby leaving human beings to do what they do best while the grunt work is taken care of by computers. Don’t believe a word of it.
Intelligent machines have already moved on from jobs that simply involve processing lots of data (compiling tax returns or reading medical charts or searching for the best value stocks) to jobs that require what used to be regarded as “the human touch.” Machines can produce plausible-sounding news reports. IBM Corp. and the Baylor College of Medicine have developed a system called KnIT (“knowledge integration toolkit”) that scans the medical literature and generates new hypotheses for research problems. Software regularly outperforms humans in predicting the outcome of court cases ranging from patent disputes to landmark Supreme Court rulings.
The great problem of management will shift inexorably from how to manage knowledge workers (who will be progressively “outplaced”) to how to manage the marginalization of knowledge workers. Ever more senior figures who have spent their lives celebrating technological progress and decrying Luddism will find themselves surplus to requirements (imagine the howl from columnists as columns are automated!) Ever more university graduates will find themselves working in the bowels of the service economy. And ever more university departments, having profited briefly from the academic arms race, will have to close as potential students realize that no number of qualifications will save them from the knowledge-worker cull.
Disappointed brainworkers have always provided combustible fuel for revolutions in the past: Look at the role that alienated intellectuals played in driving the Russian revolution or downwardly mobile graduates played in the rise of Nazism in Germany. From a social point of view, the next wave of technological progress is likely to prove the most disruptive yet.
The rise of the trillion-dollar trust fund baby
In the next decade or so we will see the birth of a new kind of baby: trillion-dollar trust fund babies who are destined to inherit fortunes that are bigger than the GDPs of small countries or the stock-market valuations of large companies.
These trillion-dollar trustafarians are the product of two trends. The first is the return of giant fortunes that are comparable with those of Rockefeller and Carnegie. The second is a concerted campaign from the right, particularly in the United States, to reduce or even abolish the inheritance tax (which conservatives have brilliantly rebranded “the death tax”). “Only morons pay estate tax,” was the proud boast of one of Donald Trump’s economic advisers, Gary Cohn, of a tax that, for 35 years after 1941, stood at 77%. Over the next 25 years about half of the $72 billion that will be passed from one generation to another will come from the richest 1.5% of households.
The rise of the trillion-dollar trust-fund baby will put yet more strain on the meritocratic idea that is the rocket fuel of capitalism. How can you talk about equality of opportunity when some people inherit fortunes that outstrip the endowments of entire universities? And how can you laud the work ethic when we have an ever-expanding permanent leisure class?
The rise of trillion-dollar babies will further tilt the overall economy away from wealth creation and toward inheritance curation: Why risk your hand at entrepreneurship when you can have a highly remunerated career as a “money-butler” to the super-rich, either as a lawyer devising ever more elaborate trusts, a political consultant lowering the inheritance tax still further or a private banker making giant fortunes even bigger still.
The next frontier of competitive advantage: genetics
The West has understandably remained nervous about exploiting the potential of genetic science since the horrors of the Holocaust. That is likely to change in the coming decades — indeed genetic science may be for the next 40 years what computer science was for the past 40 years.
There are lots of reasons for this. Genetics has been advancing at an astonishing rate since the sequencing of the human genome, not just as an abstract science but as a set of technologies. The unease engendered by the memories of the 1940s is fading. Genetic screening for abnormalities is now commonplace, and is sometimes followed by the termination of pregnancies. The fashion for enhancing your body with computer parts is spreading from university-based sub-cultures into wider society. What will really tip the balance, however, will be China, which has already tolerated the selective abortion of millions of female fetuses, and where researchers sparked controversy by editing the genome of a human embryo. Notwithstanding the subsequent official condemnation of that work, China will surely be tempted to exploit the military, and perhaps the commercial, possibilities of genetic science.
This will put a series of profound questions at the heart of business (and create a thriving sub-discipline in management ethics). What limits should the West place on genetic research? Should we impose tighter limits on the IVF industry? Or should they be free to sell, in effect, genetically superior offspring? Should insurance companies be given access to DNA tests that predict an individuals’ potential to fall ill? And should regular companies be able to select their employees based on “polygenic scores,” based on computerized surveys of thousands of genetic differences that predict their ability to thrive in their jobs? Can the West retain its focus on individual rights in the face of an economic and military competitor which might use genetic screening to discover and even create superior human beings? Or will further abandoning liberal individualism be just another price we have to pay in order to remain competitive?
The new road to serfdom
The great clarion call of market societies is freedom: freedom to exchange the fruits of our labor in the marketplace for goods and freedom to express our views in the marketplace of ideas. Yet there is a growing risk that we are losing our freedoms not only to a new generation of intellectual censors but to watchers who monitor our every move. Friedrich A. Hayek warned that the road to serfdom was being paved by the state — and certainly the Chinese government has led the way to our current dystopia with its construction of the world’s most elaborate surveillance society. But the great free marketeer failed to reckon with the opportunism of the private sector. Internet giants grow fat by sucking up information about our spending habits and selling it to third parties. Corporations increasingly used spyware of various kinds to monitor their workers ever more closely and sanction them if they paused in their productivity.
If the road to hell is paved with good intentions, the road to serfdom is paved with minor conveniences. Consumers wanted the “free services” that Google and its fellow surveillance capitalists offered (smilers with knives underneath their coats, to borrow a phrase from Chaucer). So, they gave them the right to spy on their lives. Workers wanted the convenience of being able to work from home. So, they allowed their employers to monitor their productivity from afar.
Can capitalism be revamped so that we can reclaim our lost freedoms without losing the benefit of our improved capacity to, say, fight crime or improve productivity? We need a new generation of management thinkers to devote themselves to thinking about this subject. Should we allow individuals to charge companies to use their data? Or should we go for the opposite approach and simply nationalize the IT giants on the grounds that private entities should not be trusted with such intimate knowledge? But alas at present the few people with the intellectual firepower and technical expertise to answer these questions either work for the IT companies themselves or for think tanks that depend on Silicon Valley money.
The best management gurus have played an outstanding role not only in identifying business problems but also in helping to solve them. Peter Drucker persuaded his readers to take more responsibility for “managing themselves” in order to cope with the disappearance of jobs-for-life and the extension of life expectancies. Michael Jensen arguably delayed the onset of the recent stagnation by unleashing the creative force of leveraged buyouts and private equity (though for a contrary view see Nicholas Lemann’s excellent Transaction Man). Clay Christensen helped young companies to take advantage of disruptive new technologies that changed the way that businesses operated.
During its first 100 years, the Harvard Business Review has been an invaluable bridge between the management theory industry on the one hand and the broader business public on the other. That bridge will be needed more than ever, given the tendency of academics to turn in on themselves and as businesses obsess over the long term. But in order to succeed, HBR will have to be more honest about why it has made such glaring mistakes in the past. It will also have to broaden its current somewhat blinkered focus — not only giving space to a wider range of voices on fashionable topics such as corporate social responsibility but also looking to the darker forces all too likely to transform business in the century ahead.
Bloomberg News provided this article. For more articles like this please visit bloomberg.com.
10. 5 Ways Our Intuition Leads Us Astray
We are not programmed to see the world in an objective manner. KEY POINTS– Frank T. McAndrew Ph.D.
- Many people feel very confident about following their intuition.
- We easily fall into predictable cognitive traps when we blindly follow intuition and disregard new information.
- We can become more socially effective by becoming aware of the limits of our intuition.
I frequently encounter people who pride themselves on their intuition. They humbly, and sometimes not-so-humbly, brag about their ability to quickly size up social situations and other people, and then make snap judgments. At the beginning of a new academic term, I have occasionally had excited students tell me how much they look forward to my class because they “know people” or are “good with people,” and they are confident that this will serve them well in pursuit of good grades in psychology courses.
I am always polite when these conversations take place, but such comments raise red flags signaling that the individual I am talking to probably is not as astute in social situations as they think they are. “Going with your gut” and believing that taking some time to process new information about others is unnecessary reflects a naivete about how we think.
Becoming aware of the limitations of our intuition and the cognitive traps that it can lead us into is essential for making us as socially effective as we can be. Knowing that intuition can lead us astray will not completely protect us from our cognitive biases, but it may make us more cautious about the conclusions we draw and more willing to change our minds as new information comes to light.
Why would our intuition be designed to ever steer us wrong?
Evolution Has Not Designed Our Minds to See the Social World Objectively
Natural selection has ruthlessly shaped our perceptual machinery to accurately decode what is going on in the physical world around us. People who could not tell where the edge of the cliff was or whether the animal at their feet was a kitten or a rattlesnake did not do very well. Modern humans who cannot be sure if a vehicle is approaching as they cross a busy street would be at a similar disadvantage. Consequently, our perceptions about the physical world are usually pretty reliable.
On the other hand, seeing the social world in a totally objective fashion may not have always been advantageous. Being acutely aware of our own shortcomings or being realistically pessimistic about our future could undermine our ability to persevere in the face of hardship and place us at a disadvantage in competition with others who saw themselves and their futures through more rose-colored glasses. Similarly, too easily finding fault with our in-groups could undermine loyalty and lead to ostracism from the group, which would have been tantamount to a death sentence in our prehistoric ancestral environment.
article continues after advertisement
And so, we came to see the social world in ways that were advantageous to us rather than as it actually is. Psychologists have identified a long list of cognitive biases that can get us in trouble; here are five that are pervasive:
We Confuse Observations with Inferences
When I lecture about this in my classes, I frequently hold up a piece of chalk and ask my students what they can tell me about it just by looking at it. Frequent responses include, “it is white,” “it will break if you drop it,” “it is cylindrical,” and “you can write with it.” Not all of these statements are observations. Seeing the object as cylindrical and white are observations, but believing that it will break if it falls or that you can write with it are inferences that are drawn on the assumption that the object is, in fact, a piece of chalk. If the object turns out to be a small piece of white plastic or a cigarette, the inferences would lead to incorrect predictions.
In this same way, we may confuse behaviors and traits that we have actually observed in ourselves and others with assumptions that we are making, and blurring this distinction can lead to misguided social decisions.
Confirmation Bias
When we believe that something is true, we work very hard at finding evidence that we are correct. It does not come naturally for us to try to disprove our beliefs by seeking contradictory evidence. Consequently, we notice and easily remember things that confirm our beliefs but gloss over stuff that contradicts them. A person who believes that a full moon results in all sorts of crazy behavior will say, “Ah-Hah!” and vividly remember incidents that fall in line with that belief, but that same individual is likely to ignore all of the times when weird stuff happens in the absence of a full moon or when there is a full moon and nothing unusual occurs.
We carry this same bias into social situations. The information that we process about other people is guided by our stereotypes of groups and our first impressions of individuals, and we are just as motivated to preserve these illusions as we would be to preserve our belief in the behavioral effects of the full moon.
In other words, we take unfair advantage of coincidences to protect our view of how the world and other people work.
Hindsight Bias
Psychology can be difficult to study because many of the conclusions drawn by researchers seem like common sense to us and we convince ourselves that this was something we already knew. So, students skimming through the textbook see information that sounds right and the upcoming test looks easy because they lull themselves into thinking that we are simply covering stuff that they already understand.
article continues after advertisement
The problem is that we all have been exposed to common bits of folk wisdom that are floating around and there are different bits of wisdom available to explain almost anything. Social psychologists have sometimes referred to this common wisdom as “Bubbapsychology.” The word is derived from an old Yiddish word for grandmother, Bobe, and it is psychology that everyone’s grandmother already knows to be true, so why bother doing research on it?
A classic example of this is the contradictory beliefs about what draws people together in romantic relationships. We all know that “opposites attract,” but we also know that “birds of a feather flock together.” Thus, a student forced to choose between these two alternatives on a multiple-choice test in a social psychology class may be in trouble if they are relying on bubbapsychology rather than on what they have learned through careful study of the textbook.
The Power of the Particular
We evolved in a world where we, or at least one of our relatives, knew everyone who mattered to us. Our ancestors had to cooperate with each other for success against out-groups, but they also had to recognize that these same in-group members were their main competitors when it came to dividing limited resources.
The cognitive skill that delivered the greatest payoff in this world was remembering details about individuals: Who was a reliable, trustworthy person, who was a cheater, and who would be a reproductively valuable mate. There was little need for thinking statistically about large numbers of unknown others, and, to this day, we like stories about individuals. The nightly news is usually a series of tales about particular people: the scandals of celebrities, the suffering of hurricane victims, and the wrangling of politicians.
Because of this, we find ourselves strongly persuaded by individual examples, and we give these a lot more weight in our deliberations than abstract but potentially more accurate information.
The Fundamental Attribution Error
One of the most durable of our cognitive biases is the fundamental attribution error. This is our tendency to hold other people more accountable for their actions than we should by attributing their behavior to internal motives or personality traits while disregarding the influence of situational constraints and other external forces on their behavior. As a result, we tend to praise and blame people more than we probably should in situations where their behavior results in good versus bad outcomes.
Curiously, we only do this when we are judging others. When explaining the causes of our own behavior, especially when it leads to bad outcomes, we are much more likely to use expressions such as “I really didn’t have much choice” or “I was just doing what I was told” to make sense of what happened.
https://www.psychologytoday.