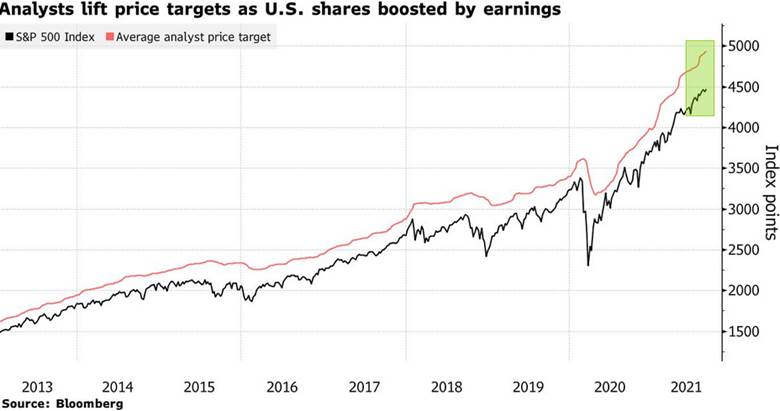
1.87% of S&P Beat Earnings in Q2—30 Year Record.
Dave Lutz Jones Trading–The second-quarter earnings season was one for the record books — 87% of companies in the S&P 500 reported better-than-expected results, a record number not matched in almost 30 years of historical data, according to Karolina Noculak, investment director at Aberdeen Standard Investments. With beats being so widespread, there’s a risk that expectations for coming quarters are too high. “Investors have now got quite accustomed to companies beating analysts’ projections”
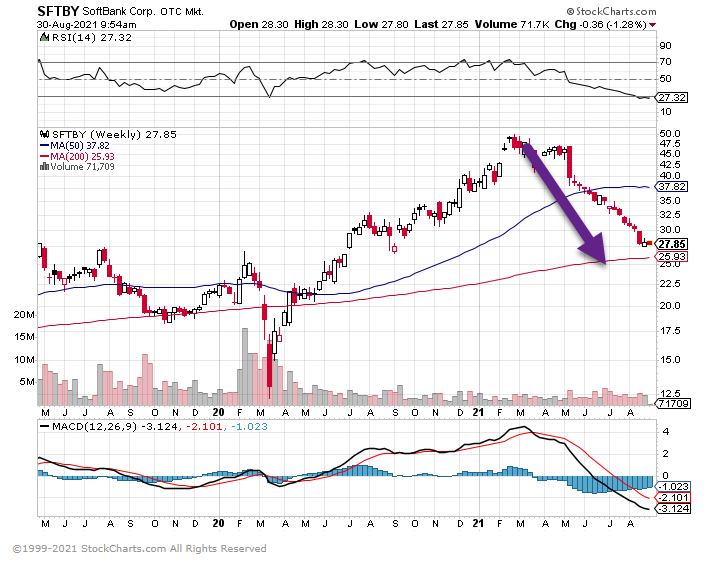
2.Softbank -44% from Highs.
SFTBY…Hit $12 during Covid.
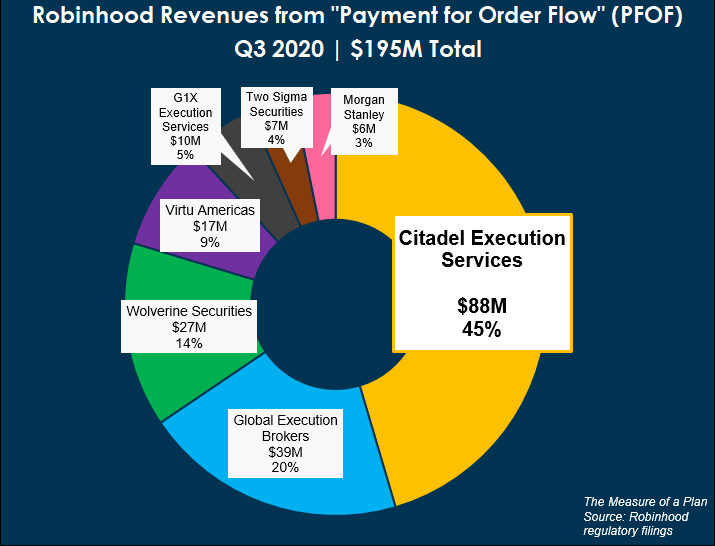
3.SEC Chairman Says Banning Payment for Order Flow Is ‘On the Table’
Last Updated: Aug. 30, 2021 at 3:35 p.m. ETFirst Published: Aug. 30, 2021 at 3:09 p.m. ET
A controversial practice that has brought in billions of dollars to brokers and high-frequency trading firms is in the crosshairs of the Securities and Exchange Commission, and could be eliminated entirely.
In an interview with Barron’s on Monday, SEC Chairman Gary Gensler said that a full ban of payment for order flow is “on the table.” Payment for order flow is a practice where brokers send trade orders to market makers that execute those trades in return for a portion of the profits.
Gensler says the practice has “an inherent conflict of interest.” Market makers make a small spread on each trade, but that’s not all they get, he said.
“They get the data, they get the first look, they get to match off buyers and sellers out of that order flow,” he said. “That may not be the most efficient markets for the 2020s.”
He didn’t say whether the agency has found instances where the conflicts of interests resulted in harm to investors. SEC staff is reviewing the practice and could come out with proposals in the coming months.
4.Aluminum Hits 10 Year High
Business Insider-Aluminum prices hit 10-year highs as supply-chain woes fail to meet surging demand-Emily Graffeo
- Aluminum futures in London climbed to $2,697 a metric ton on Monday, the highest point since 2011.
- The metal is up roughly 80% from May 2020, when the pandemic crushed sales volume.
- A lot of the aluminum supply is trapped in Asia while US and European companies face supply chain challenges.
Aluminum prices are reaching 10-year highs as a supply chain rattled by challenges fails to meet surging demand.
Aluminum futures in London climbed to $2,697 a metric ton on Monday, the highest point since 2011 for the metal used in beverage cans, airplanes, and construction. The price represents a roughly 80% jump from the low point in May 2020, when the pandemic snarled sales to the transportation and aerospace industries.
While there is enough aluminum to go around globally, much of the supply is trapped in Asia as US and European buyers struggle to get their hands on it, according to a report from the Wall Street Journal.
Shipping ports like in Los Angeles and Long Beach are jammed with orders, while containers that are used to move the industrial metals are in short supply, the Journal said. Shipping rates are also skyrocketting in a trend that’s good for shipping companies, but bad for customers who have to face rising costs.
“There’s just not enough metal inside of North America,” Roy Harvey, the CEO of aluminum company Alcoa told the Journal.
Aluminum’s rally paints a stark contrast between other commodities including Copper and Lumber, which have seen their prices scale back as supply and demand equalizes a year and a half into the pandemic.

https://markets.businessinsider.com/commodities/aluminum-price
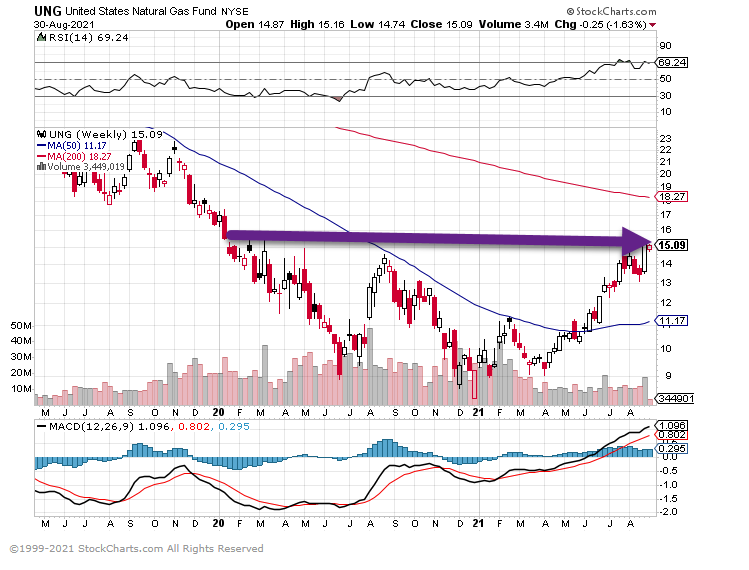
5.Natural Gas Breaks Above Downtrend Line Going Back to 2019
UNG Natural Gas Fund breaks red downtrend line
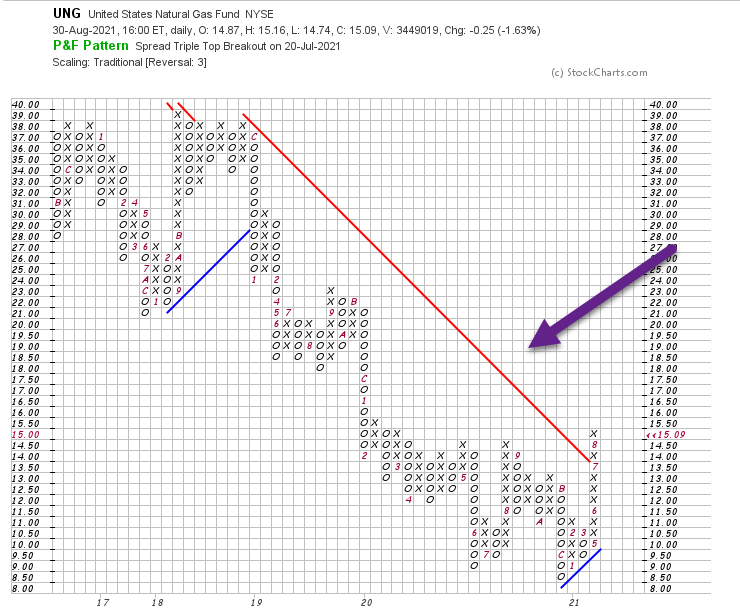
Rallies back to 2020 highs
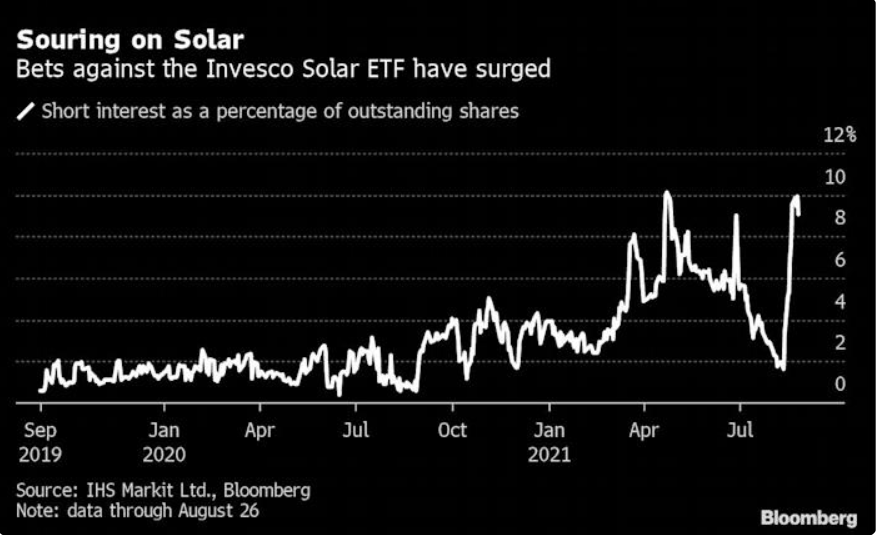
6.Solar ETF Short Interest Hits 10%
Traders Sour on Clean Energy as Bets Against Invesco ETF Surge
Elaine Chen
(Bloomberg) — A hot Wall Street trade is cooling down as supply-chain chaos emboldens short bets against one of Invesco Ltd.’s clean-energy ETFs.
With the green industry facing all manner of logistical snafus, as many as 9.9% of outstanding shares in the $3 billion Solar ETF (ticker TAN) were on loan to short sellers last week, according to data from IHS Markit Ltd. That’s the highest level since April, when short interest reached 10.1% just before the fund slumped 25%.
TAN was a big winner from the frenzy into ESG funds that followed the election of President Joe Biden, but flows have dried up and it’s on course to lose cash for the sixth month out of seven. That’s proving a drag on the whole sector, with clean-energy exchange-traded funds overall set to see assets decline for the second consecutive month, according to Bloomberg Intelligence.
The global solar industry is confronting a slew of challenges, from logistical headaches like elevated freight costs to supply-chain disruption stemming from tensions between the U.S. and China. Costs have jumped this year, creating a double blow for companies that face both a drop in demand from consumers and reduced margins.
“Investors may be concerned that solar companies aren’t really in a place to solve these short-terms issues around policy uncertainty, trade uncertainty as well as general macroeconomic trends,” said Pol Lezcano, an analyst with BloombergNEF.
The headwinds add to a roller-coaster year for TAN. Investors flocking to products with higher environmental, social and governance standards spurred assets to a record $5.2 billion in January. But they’ve pulled back amid bubble fears and to ride other market trends like cheap value shares. The ETF is down 18% this year after surging 234% in 2020.
Other funds that focus on clean energy broadly — such as the iShares Global Clean Energy ETF (ICLN) and the Invesco Wilderhill Clean Energy ETF (PBW) — have also fallen this year. While short interest has not jumped in these products to as high a level as TAN’s, inflows have slowed dramatically or reversed.
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
Subscribe now to stay ahead with the most trusted business news source.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/traders-sour-clean-energy-bets-153230489.html
TAN ETF -30% from highs

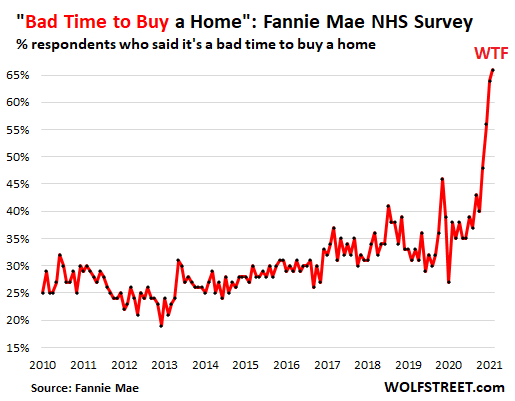
7.Americans concur: Terrible time to buy a home, perfect time to sell.
Wolf Street-This is still a historically perfect time to sell a home, after prices have spiked at a record pace and are now sky-high, though they dipped a little; and mortgage rates are still historically low, though the Fed is now mumbling about trimming back its support for mortgage rates by ending QE; and supply of homes on the market is still low, though it has been rising all year.
And Americans concur: It’s a terrible time to buy a home. According to Fannie Mae’s monthly National Housing Survey for July, which started tracking buying and selling sentiments of homeowners and renters back in 2010, a record 66% of the respondents said that “It’s a bad time to buy a home”:
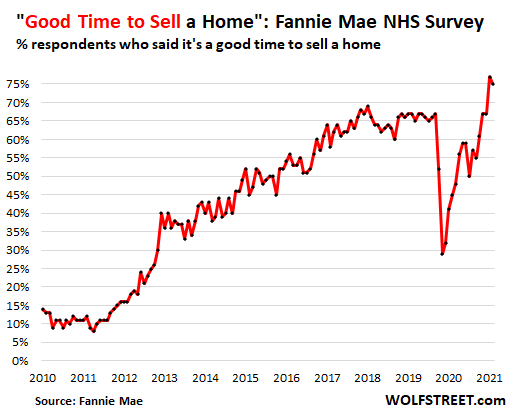
And 75%, the second highest after June’s 77%, said that “It’s a great time to sell a home”:
Home Prices Dip for First Time off Crazy Spike
https://wolfstreet.com/2021/08/23/home-prices-dip-for-first-time-from-crazy-spike-price-reductions-surge-sellers-come-out-of-woodwork-inventories-supply-keep-rising/
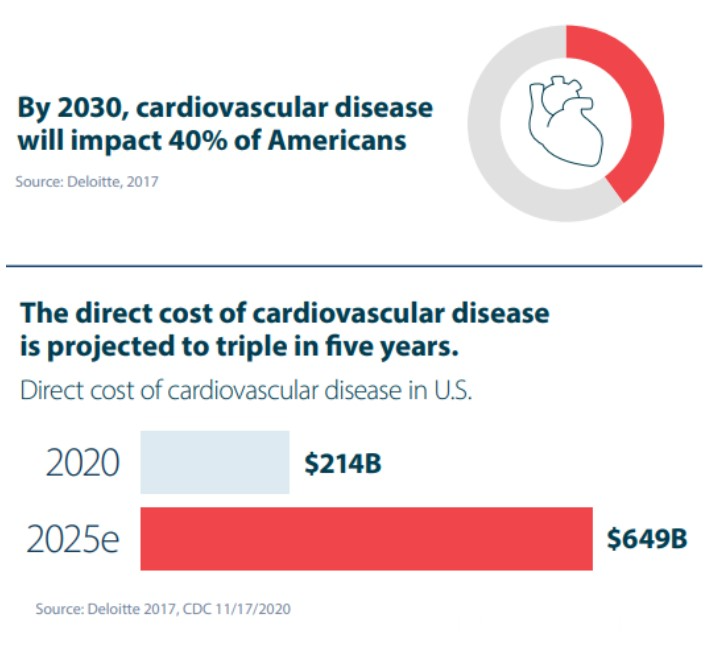
8.By 2030 Cardiovascular Disease will Impact 40% of Americans.
Talk Your Book: Investing in Dual Impact ETFs-Posted August 9, 2021 by Ben Carlson https://awealthofcommonsense.com/2021/08/talk-your-book-investing-in-dual-impact-etfs/
9.23 Corrupting Piracy Statistics You Must Know in 2021
Branka Vuleta
Global online piracy has been on the rise for years now. Consumers are continuously looking for new ways to stream or download their favorite movies, TV shows, or songs for free. Therefore, it’s not surprising that some of them try illegal methods to achieve their goal. In this article, you will learn about the latest piracy statistics that will shed some light on how online piracy works and how much it’s widespread. Let’s dive into it.
Top Online Piracy Facts and Stats in the USA (Editor’s Choice)
- Pirated videos get over 230 billion views a year.
- The USA has the most visits to piracy sites.
- Pornography is the most pirated content.
- 71,000 jobs are lost in the USA due to online piracy.
- 16% of the software on personal computers in the USA is unlicensed.
- 70% of online users find nothing wrong with online piracy.
- 34% of Gen Zers use stream-ripping.
Intriguing Piracy Statistics in 2020
Make no mistake about it, online piracy is more than just downloading files. These statistics will show how much online piracy is involved in our everyday life.
1. Pirated videos get over 230 billion views a year.
The latest piracy stats show that new TV episodes are the most favorite thing to pirate, having over 12.8 billion views in the USA and 170.6 billion views globally. There are 26.6 billion illegal views of movies produced in the States and 126.7 billion views of American TV shows.
2. By 2022, online TV and movies will lose over $50 billion in revenue.
The global online TV and movie industry will continue to lose revenue in the future. According to online piracy statistics, the movie and TV industry will lose $51.6 billion to online piracy by 2022.
3. “Game of Thrones” is the most-pirated TV show.
We all know that “Game of Thrones” was one of the most epic TV shows globally (for those who watched it, at least). That said, piracy facts like this one won’t come as a shock for all the GOT fans. The final season premiere of GOT was pirated more than 54 million times in 24 hours. The other most pirated TV shows are Rick and Morty, My Hero Academia, The Walking Dead, and SpongeBob SquarePants.
4. At 35.8%, pornography is the most pirated item on the web.
Recent piracy stats show that pornography corporations have been hit hard, with over 35.8% of their content pirated online. Movies are not that far behind with 35.2%.
5. In May 2019, superhero movies were the most pirated content.
Maybe we need a superhero to stop online piracy. According to the online piracy statistics in 2019, superhero movies were the most pirated movies. “Avengers: Infinity War,” leading the way with 5.29 million illegal downloads, “Captain Marvel” comes in second with 4.09 million, and the third most pirated movie of 2019 was “Aquaman” with 3.85 million downloads.
6. Millennials are most likely to find pirating normal.
According to digital piracy statistics, the millennial generation is most likely to consider piracy normal. Several factors contribute to this normalization, such as their pro-sharing attitude and preoccupation with the online world.
7. TV and film piracy costs the industry up to $71 billion annually.
If we take a look at the US Chamber of Commerce’s media piracy statistics in 2019, we can conclude that TV and film piracy costs the industry between $29 billion and $71 billion every year. Moreover, if we throw illegal sports live streaming into the mix, the total sum is a whopping $229 billion.
International Piracy Statistics
8. The United States has the most visits to piracy sites.
The piracy rate in the USA is growing as we speak, so it comes as no surprise that this country leads the way with over 17 billion visits to piracy sites. In Europe, Russia has over 14 billion visits. Some other European countries like France and Turkey have around 7 billion visits, while Ukraine and the United Kingdom stand at around 6 billion. Germany has somewhere over 5 billion visits. In Asia, Indonesia is the leading country with 6 billion visits to piracy sites.
9. Between 230,000 and 560,000 jobs are lost due to digital video piracy in the USA.
It’s important to note that piracy is a real threat to people involved in the entertainment industry. Thousands of people in the music industry lose their job due to piracy in the States. According to statistics on piracy, digital video piracy has dealt a blow to the United States economy, resulting in between 230,000 and 560,000 job losses and $47.5 billion and $115.3 billion in reduced gross domestic product per year.
10. According to a 2017 survey, $315 million in book sales were lost due to ebook piracy.
The global piracy statistics show that ebook piracy is on the rise. The Egyptian Publishers Union found that piracy costs Egypt publishers $16.8 million every year. The UK Intellectual Property Office found that in 2017, 17% of all ebooks downloaded that year (4 million books) were pirated. However, pirate numbers on ebook piracy show a decline in every European country except for Germany.
Music Piracy Statistics
11. The price is the most common reason for downloading pirated music worldwide.
The main reason why some people justify downloading music from illegal sites is the price. Piracy statistics have shown that 32% of music consumers do it because they think the price is too high. Another 18% say that it’s more convenient to download music that way, 16% list the sound quality as the reason, and 10% do it because music is not available through legal channels.
12. More than one-third of music listeners still pirate music.
In 2018, IFPI conducted global research exploring how consumers engaged and accessed music across licensed and unlicensed platforms. It was reported that 27% used illegal methods to listen to music. One of the many interesting piracy facts is that 23% of consumers used illegal stream-ripping. Stream-ripping has been a major concern for the music industry for years now, filing multiple lawsuits against different Russian operators.
13. In 2019, 27% of music consumers accessed unlicensed music.
According to internet piracy statistics in 2019, 27% of consumers listened to pirated music, which was a 10% drop from the year before.
14. 34% of the Gen Z generation use stream-ripping.
According to worldwide piracy statistics in 2019, 23% of users between 16 and 64 years of age opted for stream-ripping to get their music, while 34% of Gen Zers used the same method. Copyright infringement was also a more frequent method among Gen Z consumers than total internet users, with 38% getting their music this way.
15. There were 17 million stream-rippers in the USA in 2018.
Have you ever wondered how do people pirate things these days? Well, stream-ripping is a type of music piracy where users go on streaming sites like YouTube or Spotify and convert a file to a downloadable copy. 46% of stream-rippers pirate songs to play them offline, and 37% do it because they don’t like the songs enough to pay for them. A study by MusicWatch on recent pirate attacks in 2018 shows that in 2018 there were 17 million stream-rippers in the United States compared to 15 million stream-rippers recorded in 2017.
Software Piracy Statistics 2020
16. Asia-Pacific region was the epicenter of software piracy in 2017.
According to a BCA study in 2017, the highest piracy rates of unlicensed software were seen in Bangladesh (84%), followed by Pakistan and Indonesia (83%). On the other hand, Japan had the lowest software piracy rate, accounting for 16%. The commercial value of unlicensed software in the Asia-Pacific region was $16.4 billion.
17. From 2015 to 2017, the software industry lost $46.3 billion to piracy.
The software industry loses tens of billions of dollars every year due to piracy. According to piracy statistics, there was a drop from 39% to 37% in the unlicensed software rate. Seeing that decline is rather encouraging, but that doesn’t undermine the fact that unlicensed software is still widely used, taking a financial toll on software providers.
18. 16% of the software on personal computers in the USA is unlicensed.
Unlicensed software is still used around the globe at alarming rates. A BSA Global Software Survey on online piracy statistics in 2018 revealed that unlicensed software accounted for 16% of the software on personal computers in the USA, costing the software industry $9.5 billion.
19. It takes 243 days for organizations to detect an unlicensed software package.
The software piracy statistics of 2019 say that the higher the rate of unlicensed software use, the higher the possibility of a debilitating malware infection. The BSA research shows that it takes around 243 days for a corporation to detect malware attacks. That said, one of the most intriguing pirating facts, as malware statistics presented, is that it takes up to 50 days to solve the problem, and it costs $2.4 million on average.
Ebook Piracy Statistics
20. American publishers lose $300 million every year to piracy.
Ebook piracy isn’t widespread in the United States only; it’s a global problem with $300 million in publisher earnings lost annually due to internet piracy. Ebook piracy doesn’t seem to have decreased over the past few years, meaning that this number can get even higher in the future.
21. 41% of adult ebook pirates are between 18 and 29 years old.
A study supervised by the anti-piracy company Digimarc and conducted by Nielsen shows that 41% of adult ebook pirates are aged between 18 and 29. In addition, statistics show that 47% are among 30 to 44-year-olds, while the other 13% are 45 or over.
22. There were 16.5 million illegal ebook downloaders in the USA in 2017.
Downloading music and movies may be popular to download, but books are no exception. According to internet piracy facts, there were approximately 16.5 million ebook downloaders in the United States in 2017, costing publishers millions of dollars in sales.
23. 4shared.com is the most used pirate site for books in the USA.
Pirating statistics show that 50% of respondents said that they used 4shared.com to access ebooks illegally, according to a 2017 study. 4shared.com is the most popular book sharing site for consumers who want to download a book illegally. Uploaded.net and Books.org are also a popular choice.
Conclusion
The above mentioned piracy statistics and facts should serve as a sign of how much global online piracy has progressed in recent years. The statistics show that companies will lose the everlasting battle with internet pirates if they fail to adapt. One thing is clear—unauthorized downloading and copying of digital material is theft.
Frequently Asked Questions
https://legaljobs.io/blog/piracy-statistics/
10.3 Habits That Will Leave You Emotionally Exhausted
Theo Tsaousides Ph.D. Smashing the Brainblocks
Thinking patterns that contribute to excess emotional weight.
Posted September 15, 2019 | Reviewed by Gary Drevitch
There are certain foods that, when eaten in copious amounts, we know will bring consequences: Our waists will expand, our cholesterol levels will skyrocket, and our doctors will give us a lecture. With respect to our nutritional practices, we are aware of which foods contribute positively to our physical wellness and which detract.
Similar to how eating certain foods can have a long-term effect on our physical wellness, thinking in certain ways can have a long-term effect on our emotional wellness. If these practices, these mental habits, were foods, we would say that they make us gain a lot of emotional weight. While there is no such metric, think of emotional weight as a state of negative affect that consists of a mix of worry, stress, and disappointment. Emotional weight can become as stubborn and tough to lose as body weight. And just like body weight can pose restrictions on the kind and intensity of physical activity we engage in, emotional weight can make it difficult to feel joy and appreciation, to be open and accessible, and to be motivated and engaged.
Here are some common practices that can add emotional weight and make a dent in our emotional wellness.
1. Setting unrealistic expectations
Expectations are beliefs about the way the world should look; for example, how we should feel, what we should have achieved, and how other people should be treating us. When expectations are unmet, they can become a significant source of frustration. When setting unrealistically high expectations, the chances of failing to meet them are also higher, which means more frustration. We typically think of unrealistic expectations in terms of setting high performance standards in certain areas of life. For example, maintaining a 4.0 GPA, getting offers from any job we apply for, or making a sale after each contact with a lead. These are relatively high standards to meet.
Unrealistic expectations extend beyond bigger goals like those. Believing that you should be able to wake up early every morning to work out because this is what successful people do, that replies to your emails should come within minutes because this is what respectful people do, or that you should be happy with what you have because this is what grateful people feel, are expectations that we set about daily things based on arbitrary rules, which can become emotional traps when things are not happening the way we think they “should.”
These tiny failures in which we or others are not doing what “should” be done can have an insidious toxic effect on our emotional wellness. Making “should” statements is often cited as one of the cognitive distortions—a pattern of illogical thinking—that contributes to the onset and maintenance of emotional challenges, like anxiety and depression. You may ask who’s to decide what is realistic and unrealistic. This is true, and labeling something unrealistic can become a deterrent for trying harder. While defining the term deserves a longer discussion, thinking of unrealistic as something that is not supported by either effort or evidence is a good rule of thumb. In other words, if we are not working diligently toward something or if there is no proof or rationale for what we expect, then it may be unrealistic.
2. Making unfair comparisons
Social comparison is a common practice and a useful tool to place ourselves in a continuum of psychosocial indicators. While there are advantages to social comparison, like ensuring that we are hitting certain developmental milestones or that we are performing well in different areas of life, like work or school, when these comparisons are unfair, they can have a negative impact on our well-being.
article continues after advertisement
Studies show that unfair comparisons can raise anxiety and depression, deplete motivation, and reduce self-esteem. Regardless of how amazing you are, there will always be people who are smarter, richer, and prettier. Upward comparison—comparing yourself to the people in a higher position on the list—could have a positive or a negative effect. It could either inspire and motivate you or it could make you feel inadequate, incompetent, and unaccomplished. Similarly, there are people who are less smart, less wealthy, and less attractive than you. Comparing yourself to them—downward comparison—tends to make a positive contribution to your self-esteem.
High school reunions used to be a great occasion for social comparison, sometimes leaving us feeling great and sometimes miserable. But in the last few years, an even more massive opportunity for social comparisons has emerged, one that you don’t have to wait for once every decade: online social networks.
These networks provide a readily available platform for social comparison, a quick way to look at how other people are doing: how many friends they have, how many great vacations they go on, how much they love their job, or how adorable their cats are. Frequent users of online social networks report a persistent feeling of disappointment and dissatisfaction with their own lives, because other people’s lives seem so much better. The important question to ask is what purpose does this kind of comparison serve and how does it contribute to growth? What can you learn from comparing yourself to others and how will it affect what you actually do, not only how you feel?
While we have a choice of either upward or downward comparison, it is important to keep in mind that comparisons, in general, are unfair because (a) we only get a glimpse of what someone has achieved but we know very little about how they achieved it, and (b) while we can compare our current state with someone else’s, we do not compare the circumstances that led to that state.
Your best friend from college, for example, may have been able to buy her own home, while you are still a renter, which may make you feel frustrated and disappointed with yourself and your lack of achievement. However, (a) your friend may be working two (unfulfilling) jobs to pay the mortgage, and (b) she may be living somewhere where the cost of buying a home is much lower. To avoid a blow to your well-being, make social comparisons that are both purposeful and fair.
3. Overcommitting
Some of us have a tendency to sign up for more than we can handle. We agree to participate in new and exciting projects, take on more responsibilities at work, volunteer for good causes, and fill our schedules with more activities than there is time to do them. We overcommit.
Overcommitting can cause overwhelming anxiety, cognitive overload, and mental fatigue. Taking on more responsibilities than we can carry out reduces the chances that any one job will get the attention it deserves and get done really well. But why do we keep doing it? There are two thinking patterns that contribute to overcommitting.
First is the belief that being busy is good. Busy people are considered more successful, more competent, and more important. Therefore, staying and sounding busy is more socially desirable than having too much free time and nothing to do. And while we can impress ourselves and others with how busy we are, the price we pay is that we now have to pencil in downtime in our schedules, we have to set reminders on our phones that tell us to take a break, and we have to use meditation apps to clear our heads so we can be even more effective at staying busy.
The other way of thinking that contributes to overcommitting is the fear of missing out (FOMO). Life is full of exciting opportunities and if you start saying no, you risk being left out and excluded from something groundbreaking, life-changing, or history-making. So, say yes now, and figure out how to work it into your schedule later. Ironically, the brief anxiety caused by FOMO is now replaced by the chronic stress that comes with having overcommitted. Focusing on finding a balance between doing too much and doing too little may take time, but it will offset the emotional weight added by the stress of overcommitting.
A good starting point to prevent emotional weight gain is awareness—becoming able to identify these practices as we engage in them. It is easy to identify foods that contribute to weight gain. We recognize a cupcake when we see it, and then we choose whether to eat it or not. But thought patterns are often hidden behind clouds of words and habits, which makes it harder to identify and change.
Therefore, a first step to avoiding the excess emotional weight is to begin recognizing when we engage in these practices, by asking ourselves questions like: Is this expectation realistic? Is this comparison fair? Is this commitment wise? After we recognize them, we can make better choices.
Facebook image: Sam Wordley/Shutterstock
LinkedIn image: fizkes/Shutterstock